Frontiers | The Potential Role of RP105 in Regulation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis During Inflammatory Diseases

Figure 1 from Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promotes osteoclast differentiation and activation by enhancing the MAPK pathway and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells. | Semantic Scholar

NLRP3 regulates alveolar bone loss in ligature‐induced periodontitis by promoting osteoclastic differentiation - Chen - 2021 - Cell Proliferation - Wiley Online Library

Thonzonium bromide inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and prevents LPS-induced bone loss in vivo - ScienceDirect
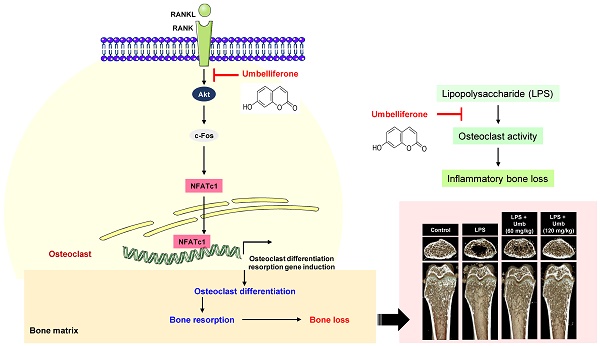
Umbelliferone Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Bone Loss and Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Attenuating Akt-c-Fos-NFATc1 Signaling

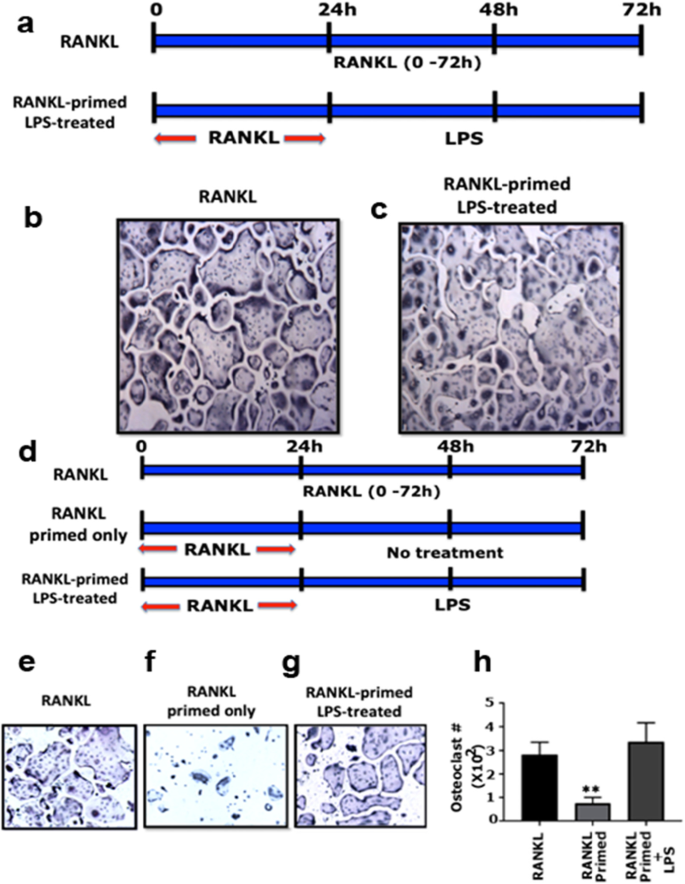
LPS induces osteoclast differentiation in RANKL-primed cells. a The... | Download Scientific Diagram

DPP-4 inhibitor impedes lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo - ScienceDirect

Betulinic Acid Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via Attenuating Akt, NF-κB, and PLCγ2-Ca2+ Signaling and Prevents Inflammatory Bone Loss | Journal of Natural Products
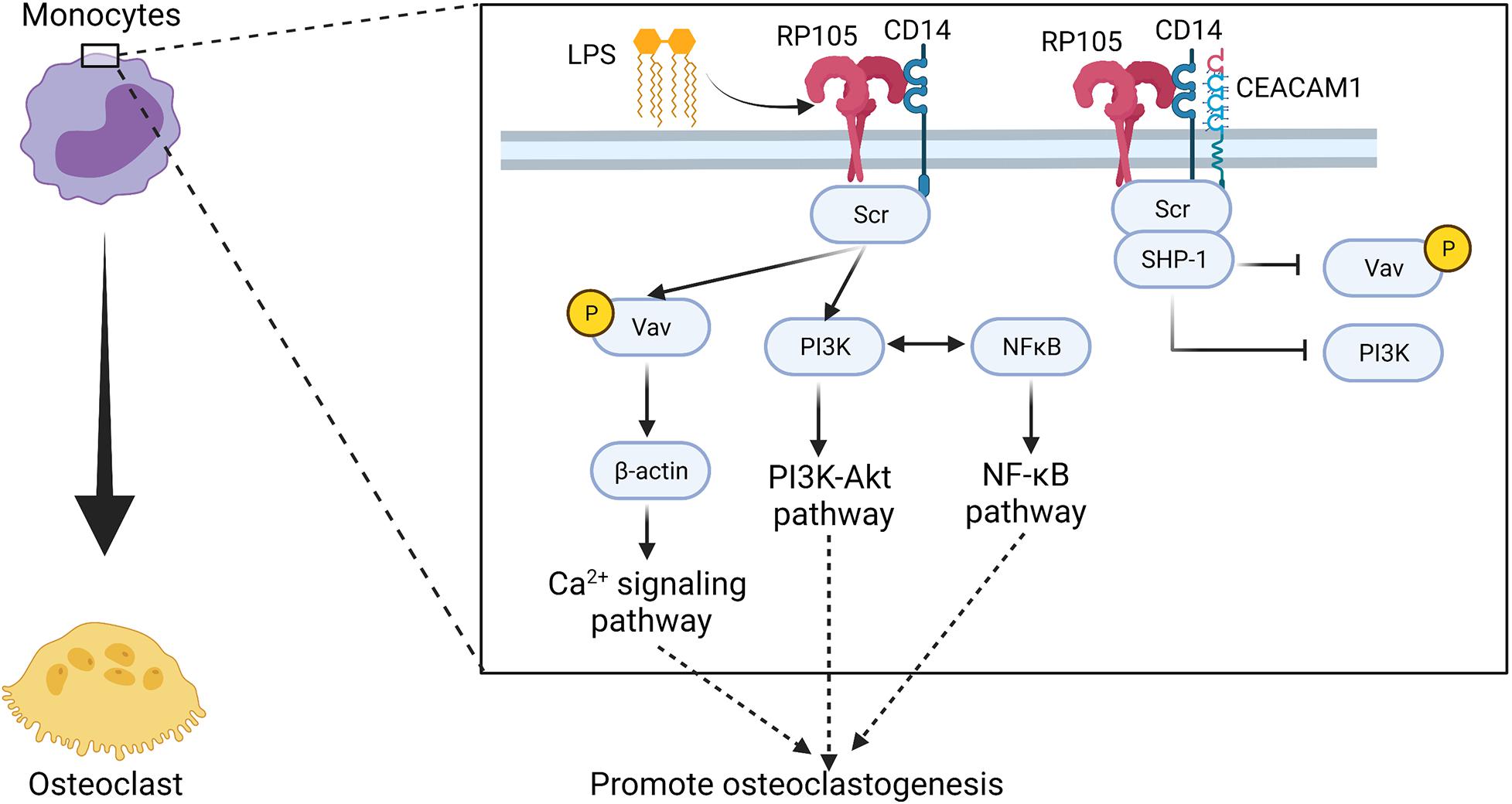
Lipopolysaccharide- TLR-4 Axis regulates Osteoclastogenesis independent of RANKL/RANK signaling | BMC Immunology | Full Text
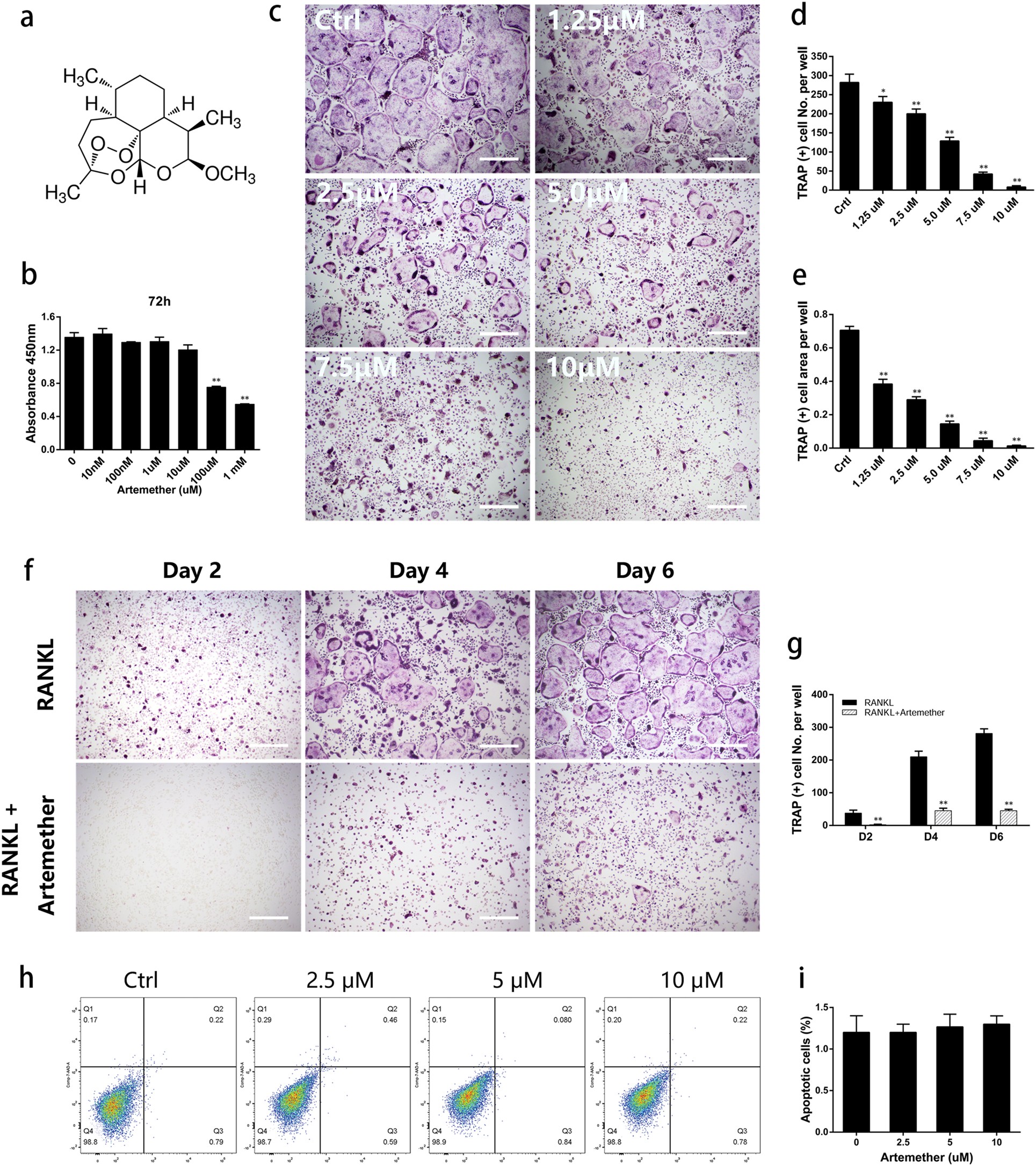
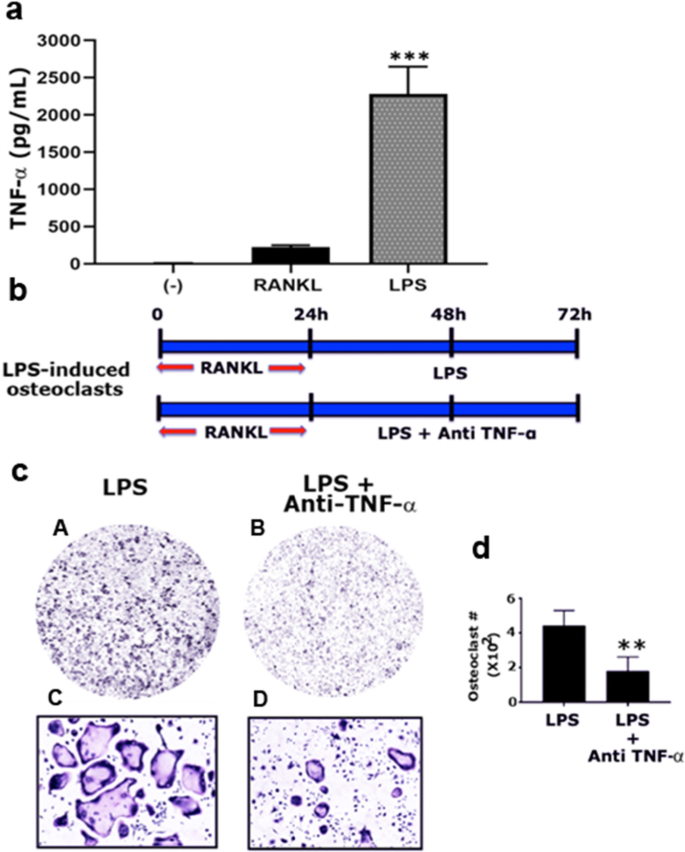
Artemether attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via suppression of MAPK signaling pathway | Cell Death & Disease

IJMS | Free Full-Text | NLRP3 Inflammasome Negatively Regulates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis of Mouse Bone Marrow Macrophages but Positively Regulates It in the Presence of Lipopolysaccharides

Dihydroartemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone loss via the mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway | Cell Death & Disease
Loss of Protein Kinase C-δ Protects against LPS-Induced Osteolysis Owing to an Intrinsic Defect in Osteoclastic Bone Resorption | PLOS ONE

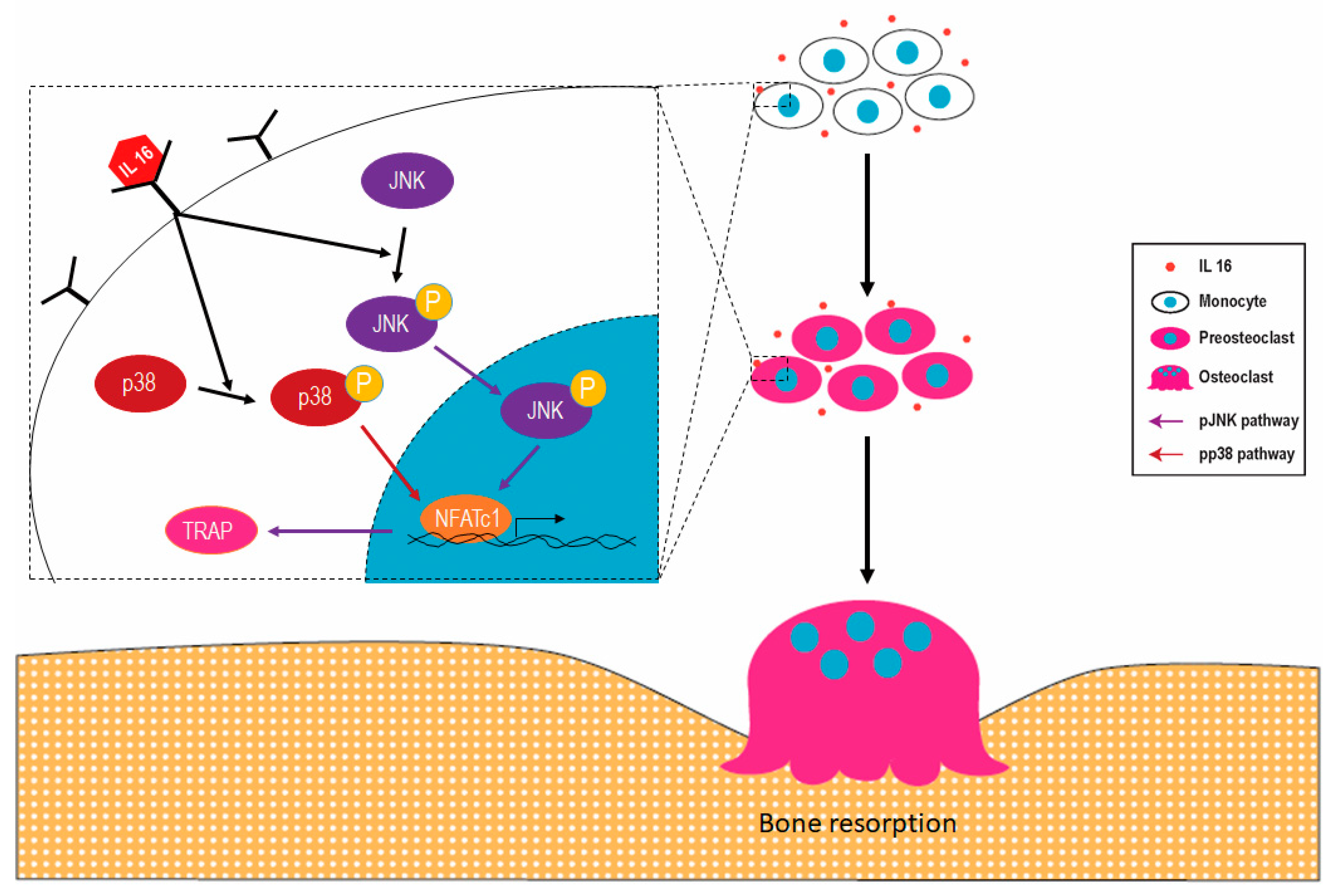
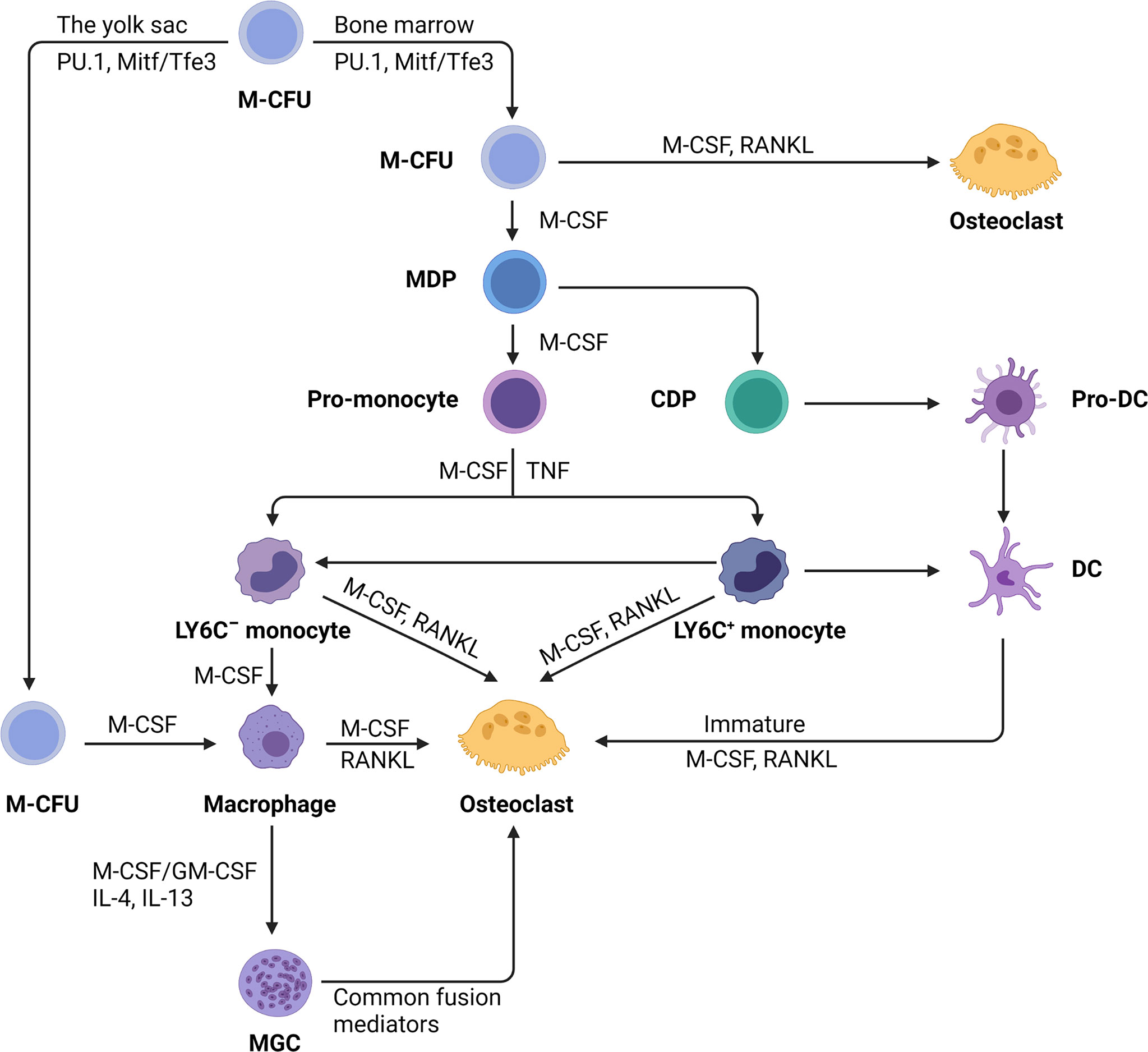
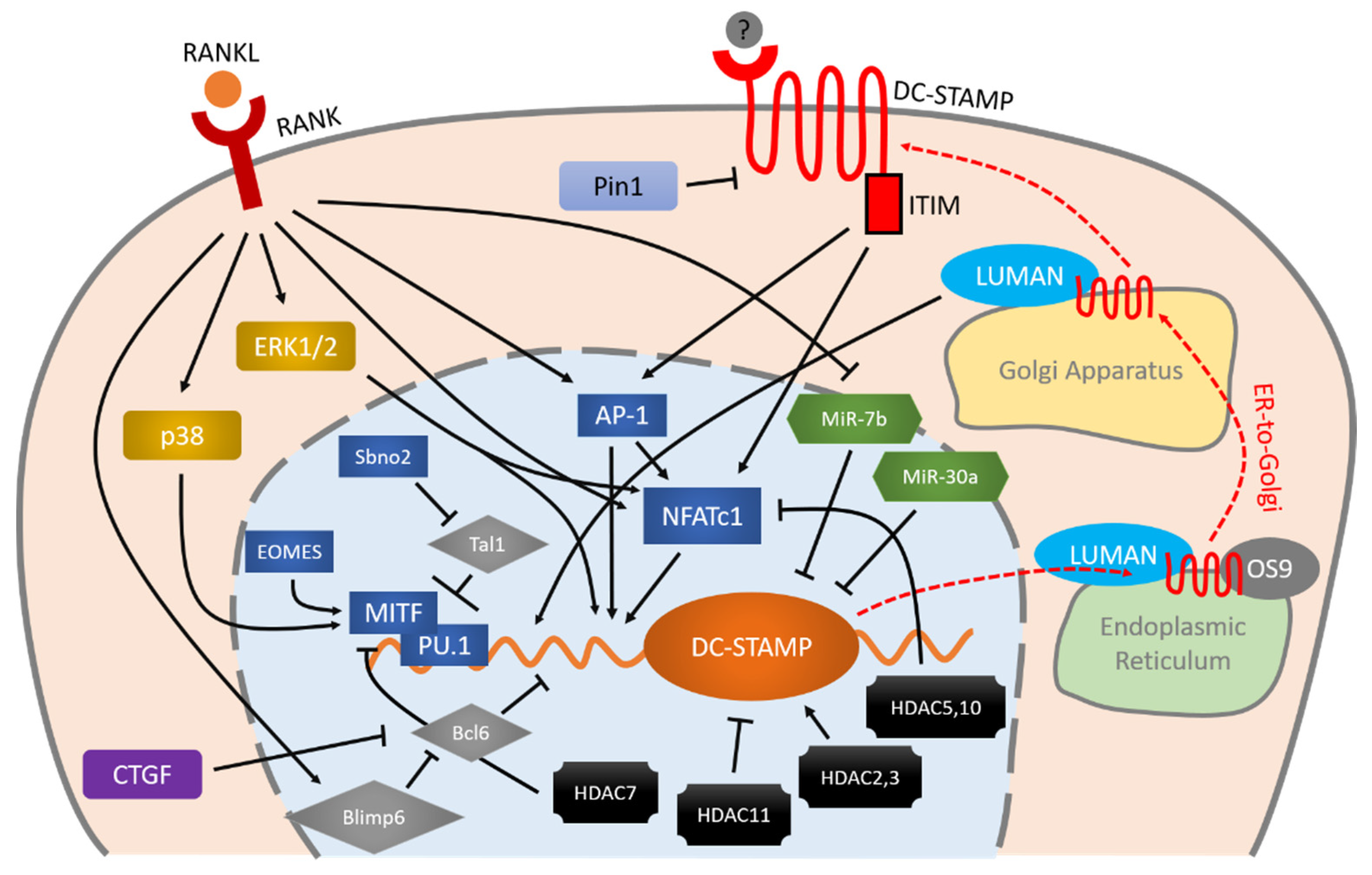
Role of Muramyl Dipeptide in Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Biological Activity and Osteoclast Activity

CGRP inhibits LPS induced-osteoclast differentiation in vitro.: (a) Raw... | Download Scientific Diagram
Lipopolysaccharide- TLR-4 Axis regulates Osteoclastogenesis independent of RANKL/RANK signaling | BMC Immunology | Full Text
Rhinacanthin C Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption: Roles of TRAF6/TAK1/MAPKs/NF-κB/NFATc1 Signaling | PLOS ONE
Epothilone B prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory osteolysis through suppressing osteoclastogenesis via STAT3 signaling pathway - Figure f2 | Aging