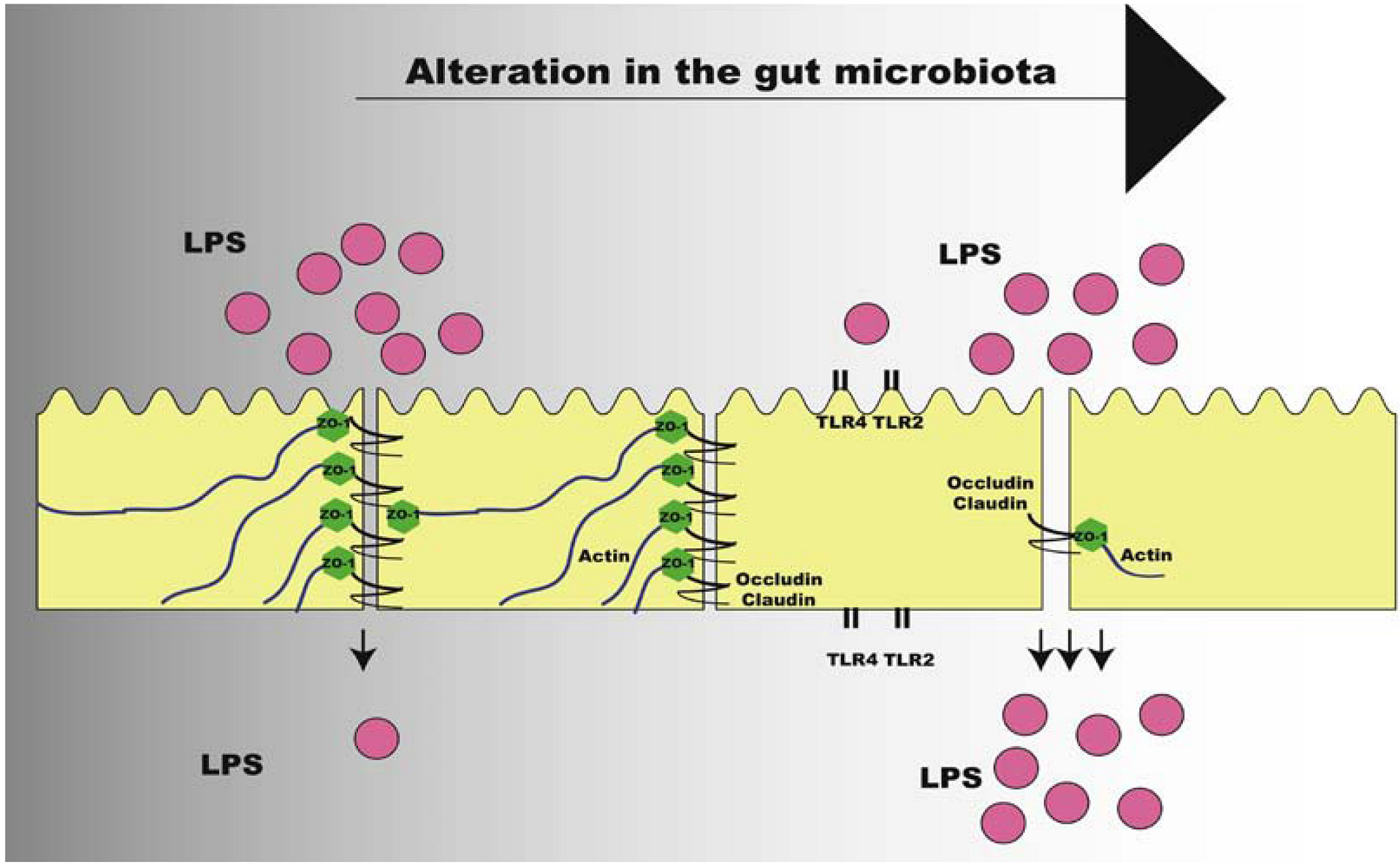
Metabolic endotoxemia: a molecular link between obesity and cardiovascular risk in: Journal of Molecular Endocrinology Volume 51 Issue 2 (2013)

Insulin- and Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Signaling in Adipose Tissue Macrophages Regulates Postprandial Glycemia through Akt-mTOR Activation - ScienceDirect

Gut-derived lipopolysaccharide augments adipose macrophage accumulation but is not essential for impaired glucose or insulin tolerance in mice | Gut

Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: history of the research and remaining questions

Insulin Sensitivity-Enhancing Activity of Phlorizin Is Associated with Lipopolysaccharide Decrease and Gut Microbiota Changes in Obese and Type 2 Diabetes (db/db) Mice | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Increased IL-1β activation, the culprit not only for defective insulin secretion but also for insulin resistance? | Cell Research

Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance | Nature Communications

Gut-derived lipopolysaccharide augments adipose macrophage accumulation but is not essential for impaired glucose or insulin tolerance in mice | Gut

Implication of inflammatory signaling pathways in obesity-induced insulin resistance. - Abstract - Europe PMC
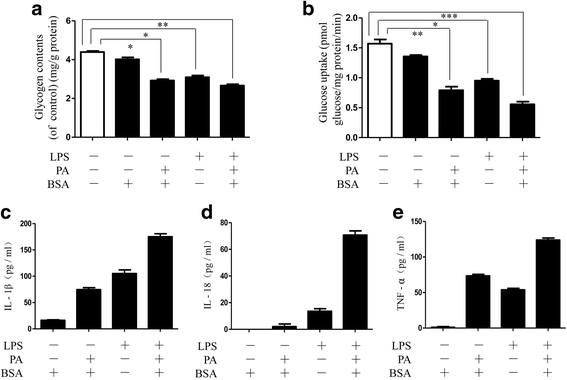
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate insulin resistance by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetes rats | Stem Cell Research & Therapy | Full Text

PPAR δ inhibition protects against palmitic acid-LPS induced lipidosis and injury in cultured hepatocyte L02 cell

JCI - Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor TLR4 requires saturated fatty acid–induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice
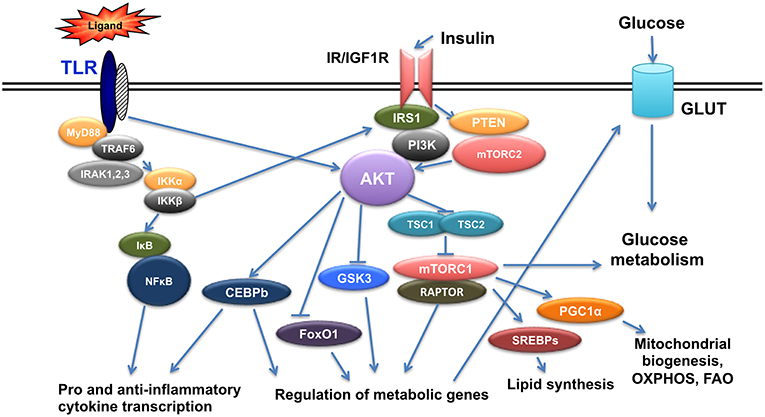
Frontiers | Insulin Signaling and Insulin Resistance Facilitate Trained Immunity in Macrophages Through Metabolic and Epigenetic Changes
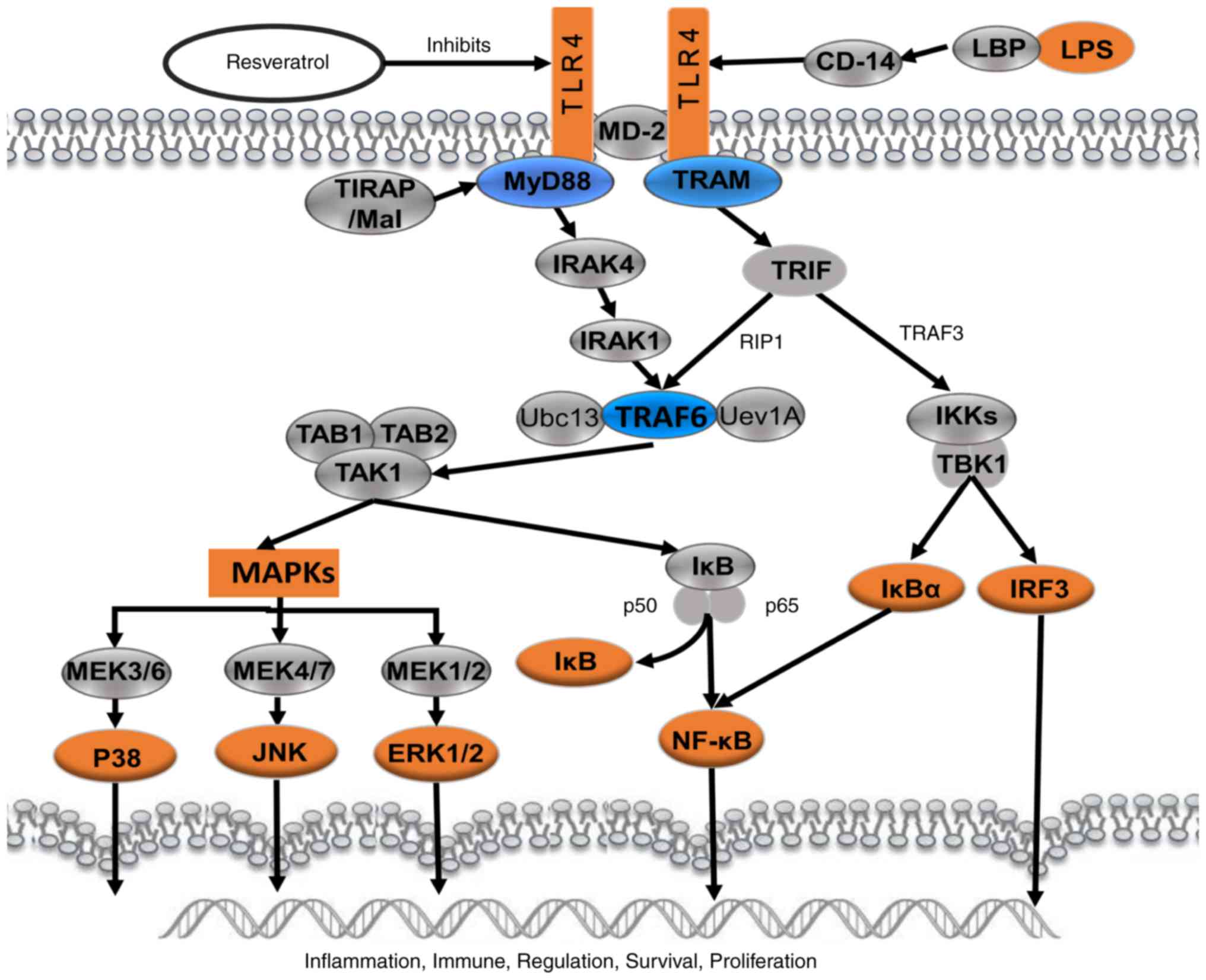
Resveratrol inhibits LPS‑induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4‑NF‑κB/MAPKs/IRF3



![PDF] Linking Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Obesity and Insulin Resistance. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Linking Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Obesity and Insulin Resistance. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1561c519bc7325fe1035f872b626720f56d90064/4-Figure2-1.png)


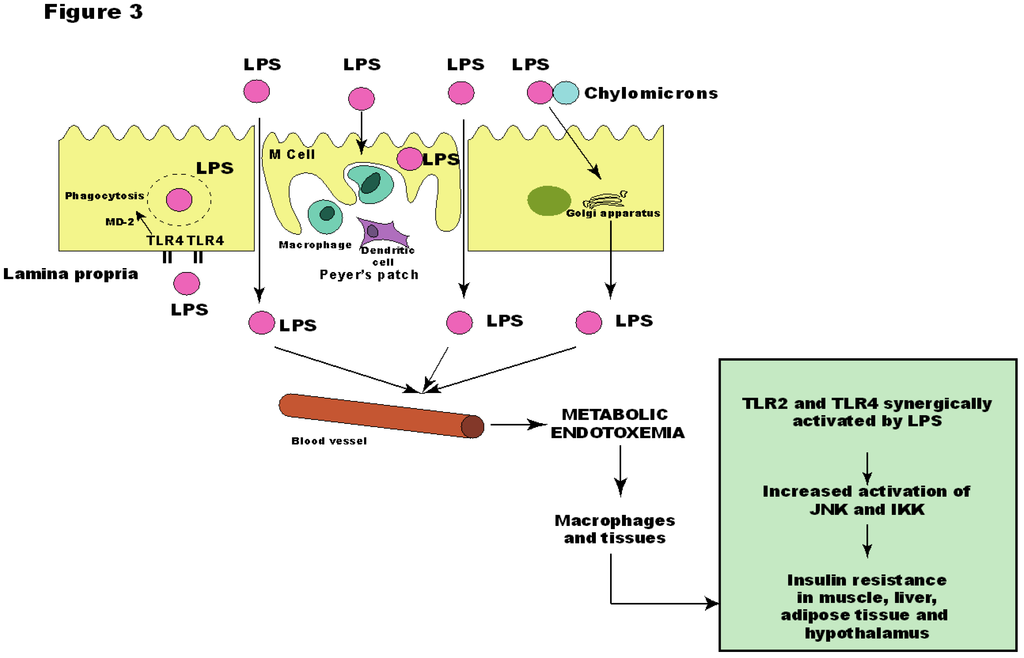


![PDF] Microbiota and LPS-Induced Obesity Inflammation: Therapeutic Implications | Semantic Scholar PDF] Microbiota and LPS-Induced Obesity Inflammation: Therapeutic Implications | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/98aba306c244bceaf0207866081dc642176ce975/7-Figure1-1.png)