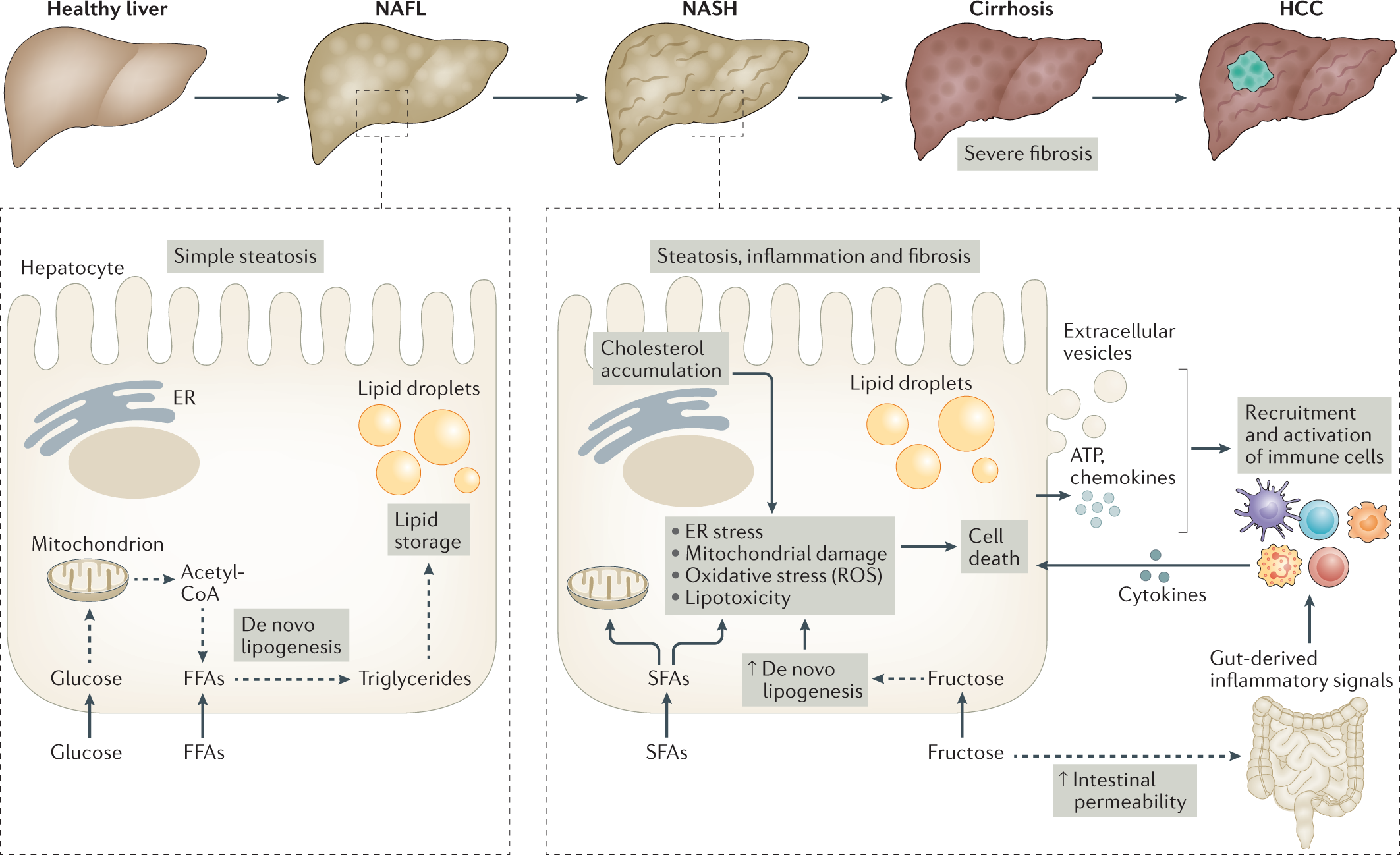
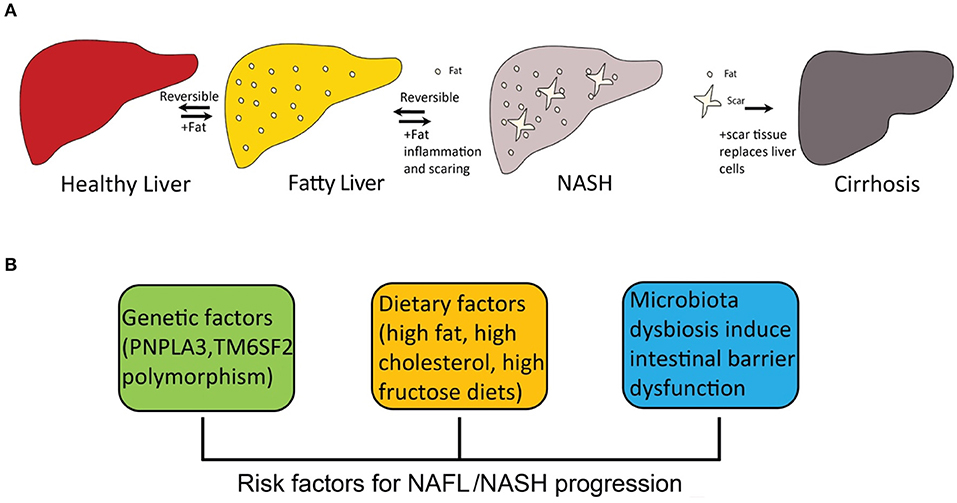
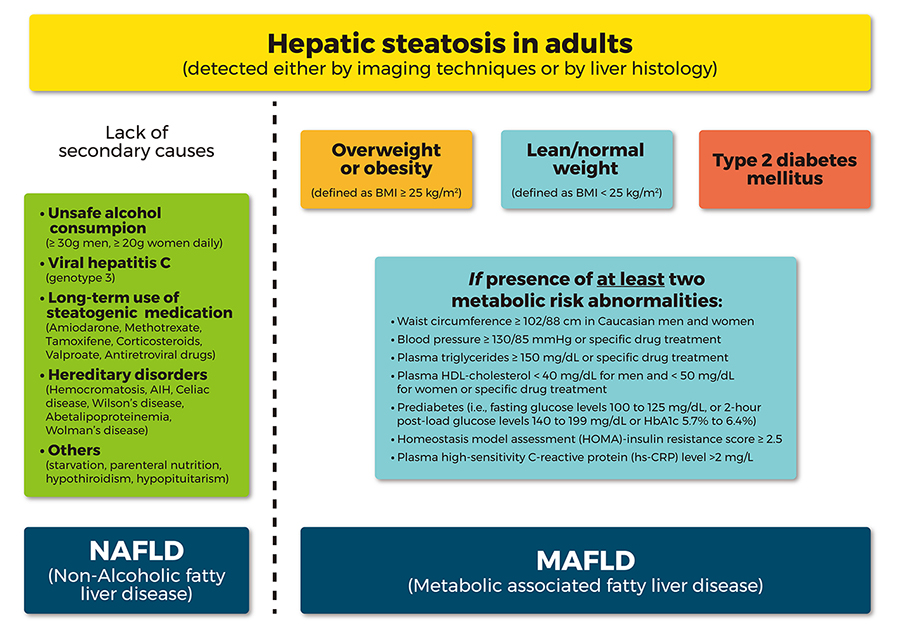
Role of hepatic fatty acid metabolism in the development of hepatic... | Download Scientific Diagram

A human pluripotent stem cell model for the analysis of metabolic dysfunction in hepatic steatosis - ScienceDirect
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is an early predictor of metabolic diseases in a metabolically healthy population | PLOS ONE

Thrombospondin 1 improves hepatic steatosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice and is associated with hepatic fat content in humans - eBioMedicine
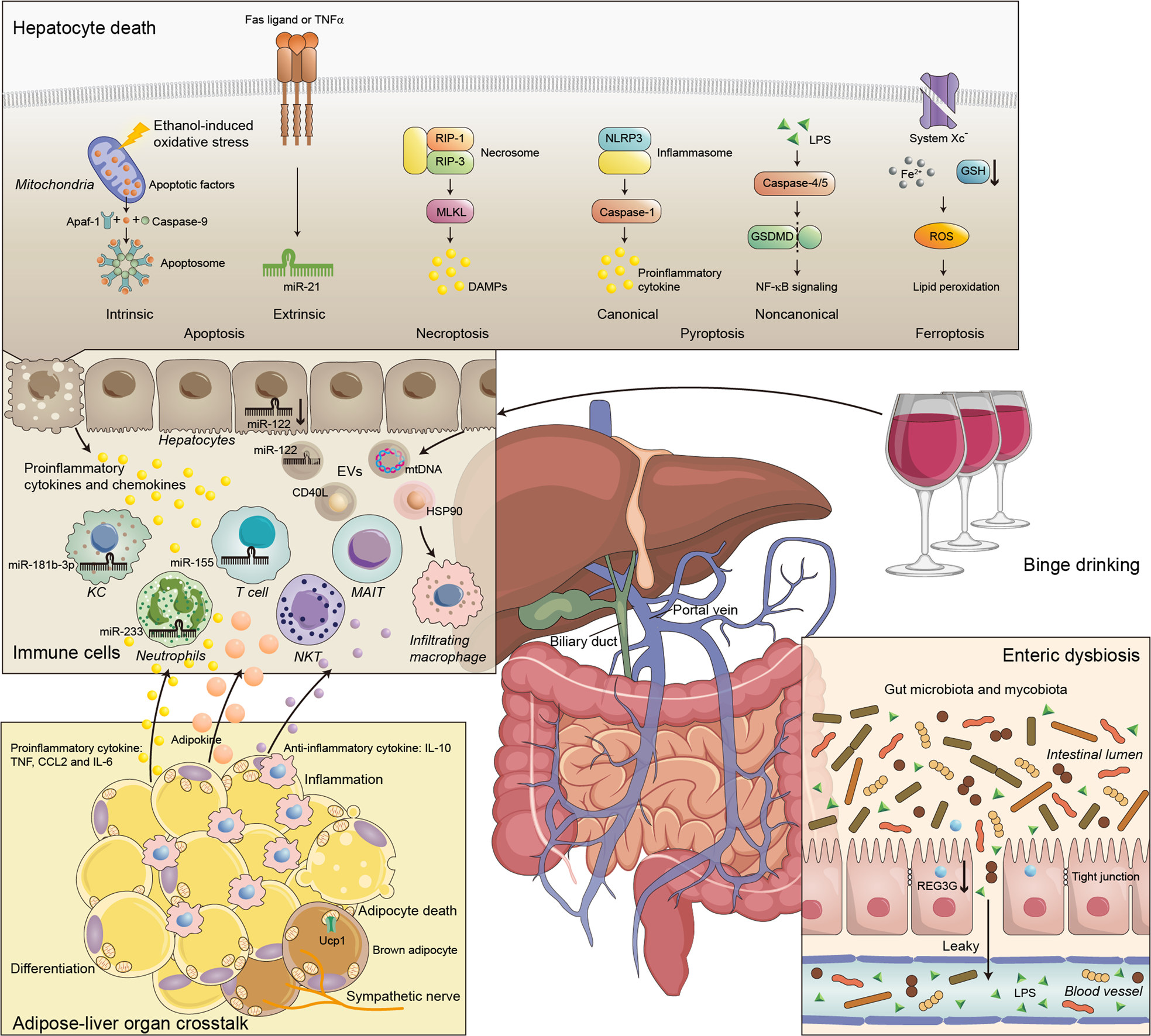
Immunological mechanisms and therapeutic targets of fatty liver diseases | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

Defining paediatric metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement - The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology
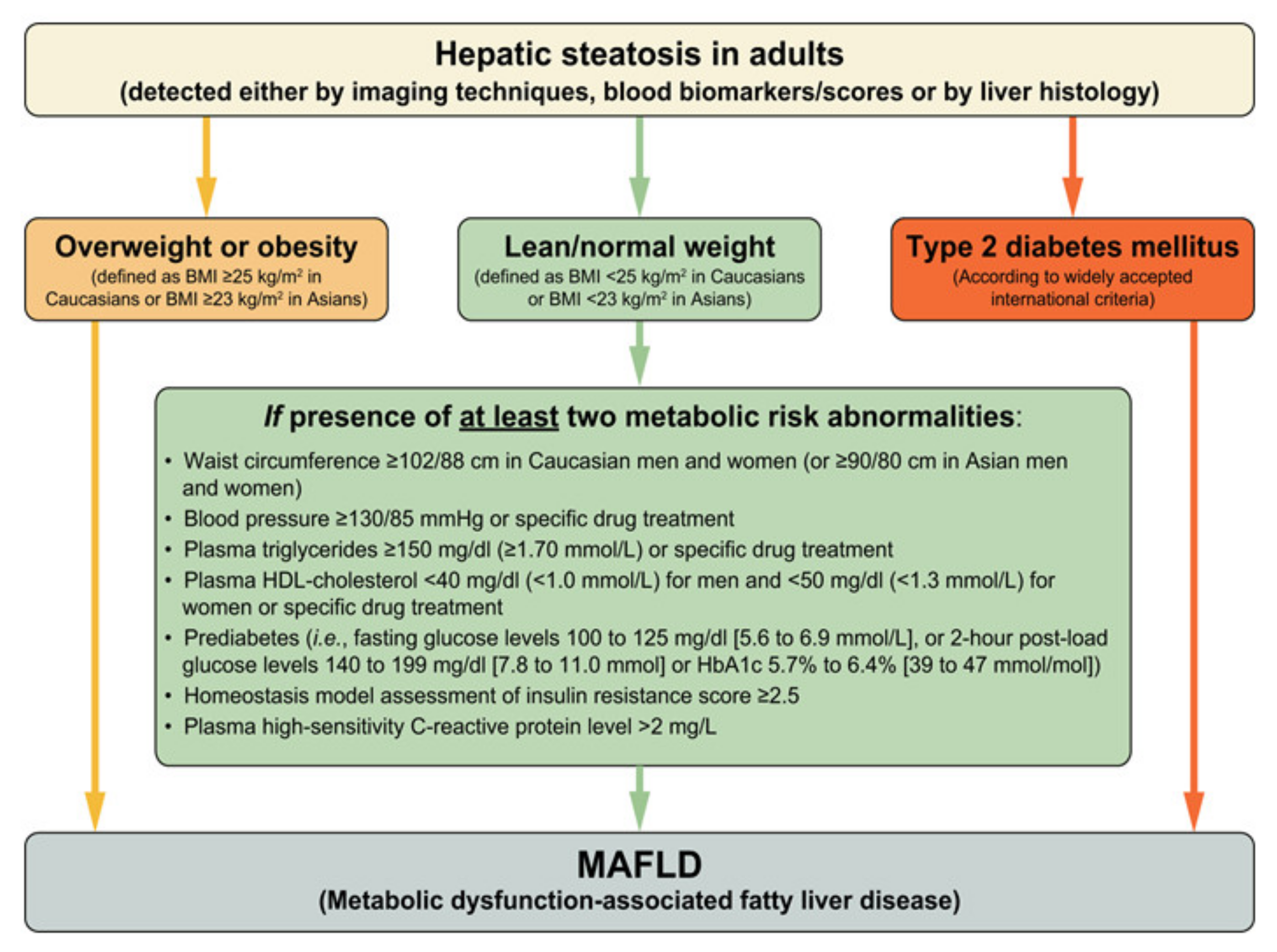
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—A Condition Associated with Heightened Sympathetic Activation
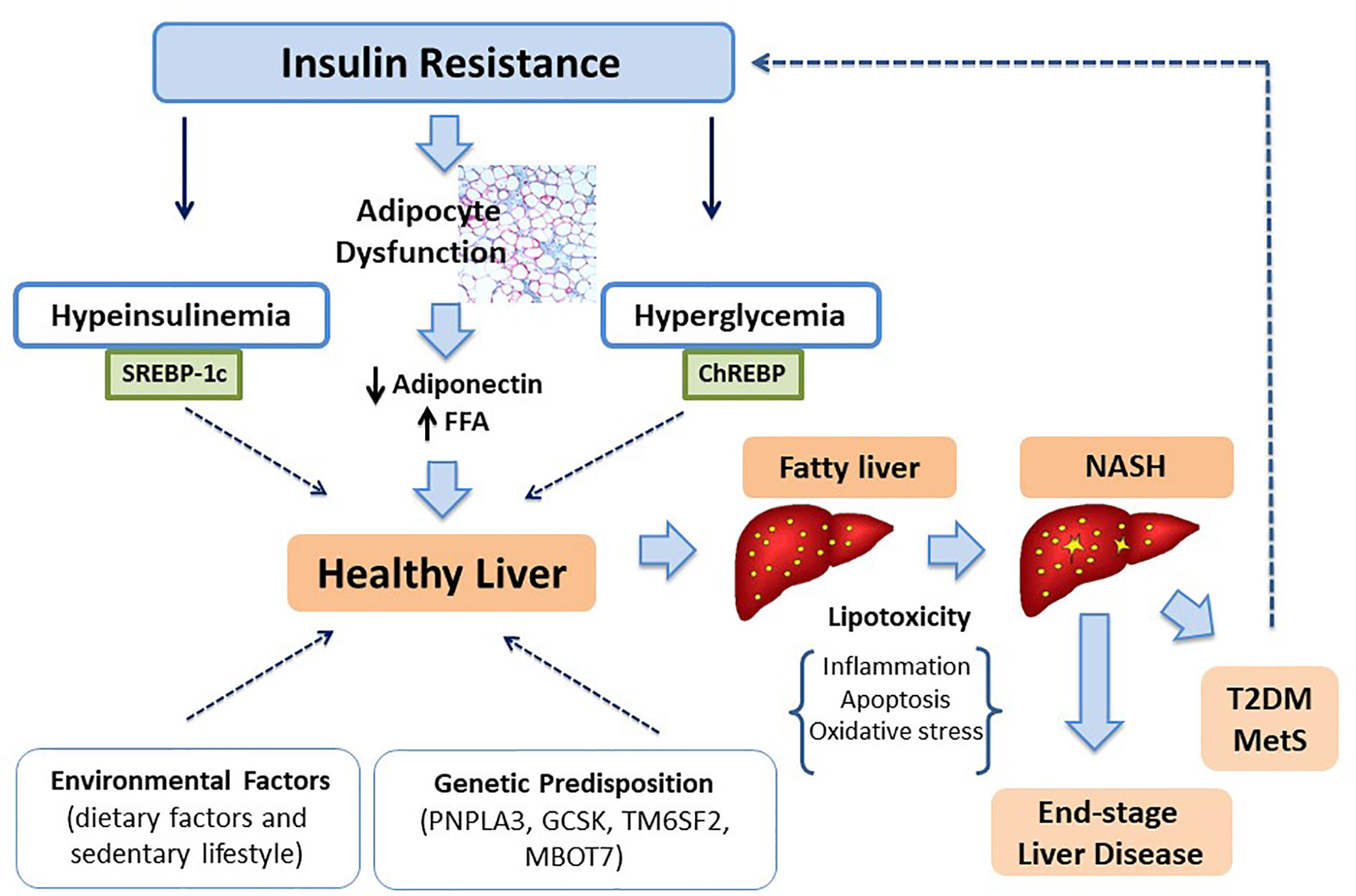
Frontiers | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Youth With Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
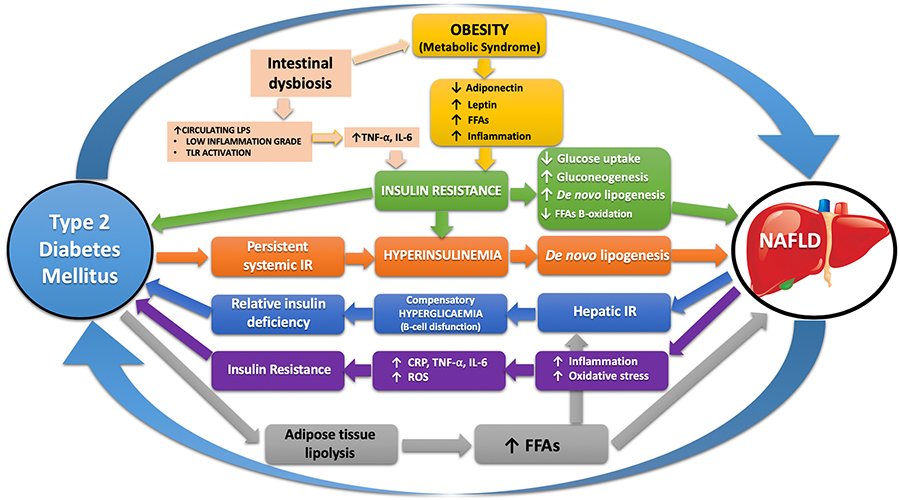
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms shared between the two faces of the same coin
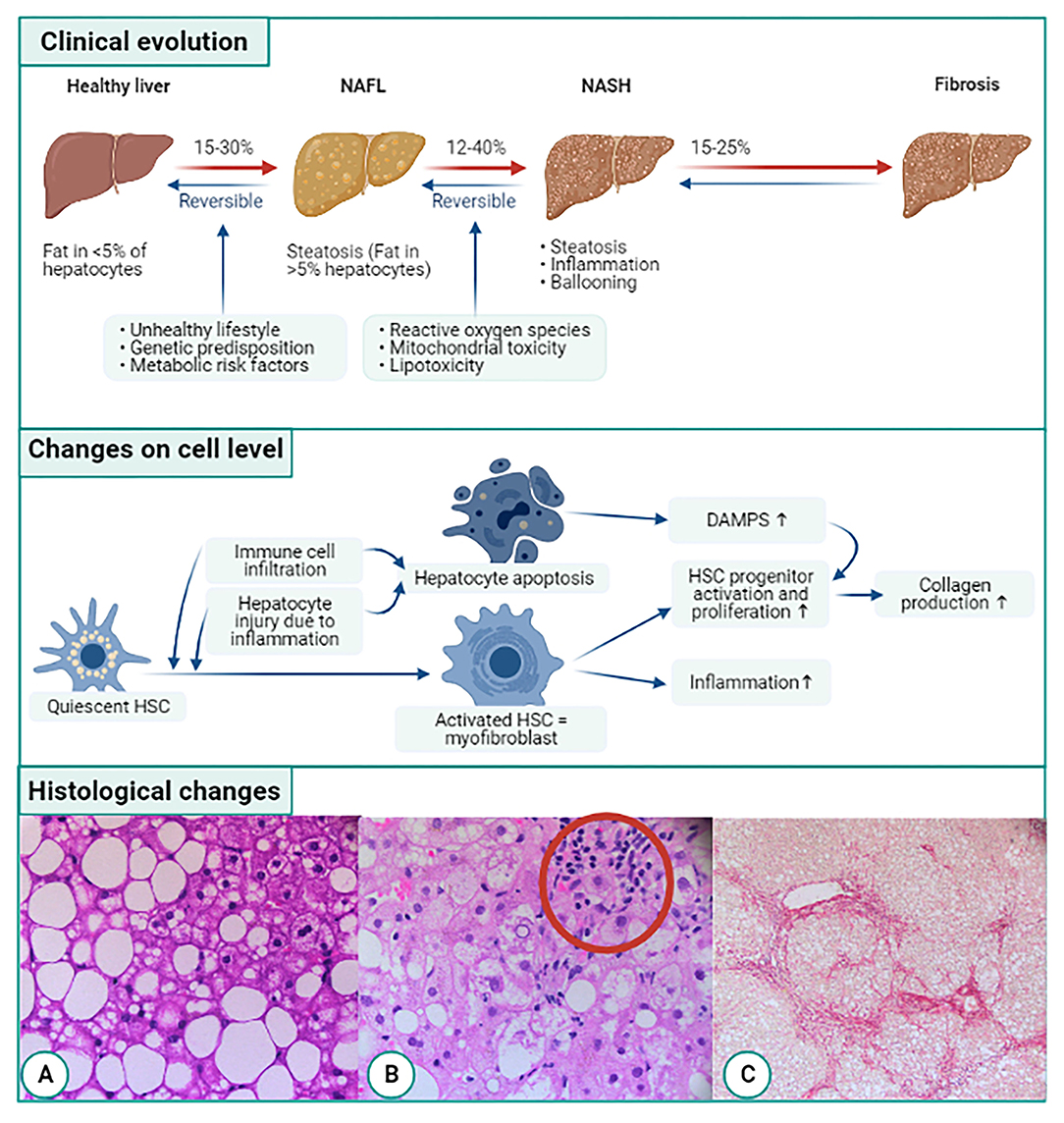
Frontiers | Liver Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Liver Biopsy to Non-invasive Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnostic and interventional circulating biomarkers in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis - Tincopa - 2020 - Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism - Wiley Online Library

Links between metabolic syndrome and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism
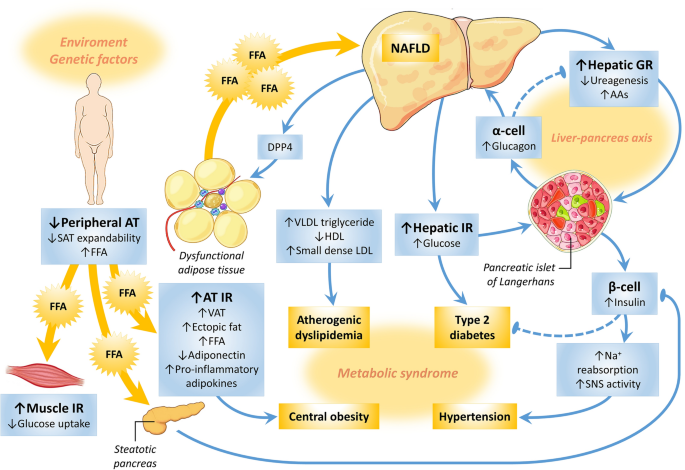
NAFLD as a continuum: from obesity to metabolic syndrome and diabetes | Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome | Full Text
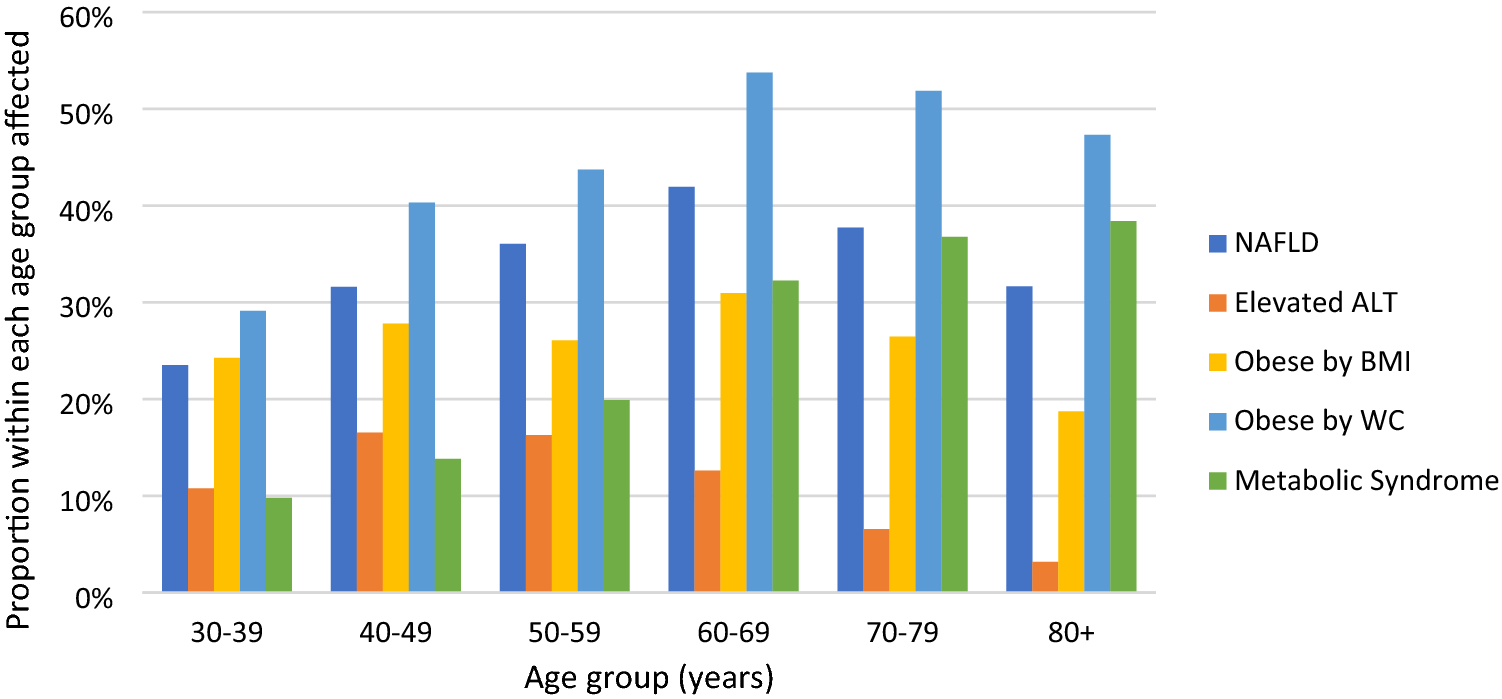
A problem of proportions: estimates of metabolic associated fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis in Australian adults in the nationwide 2012 AusDiab Study | Scientific Reports
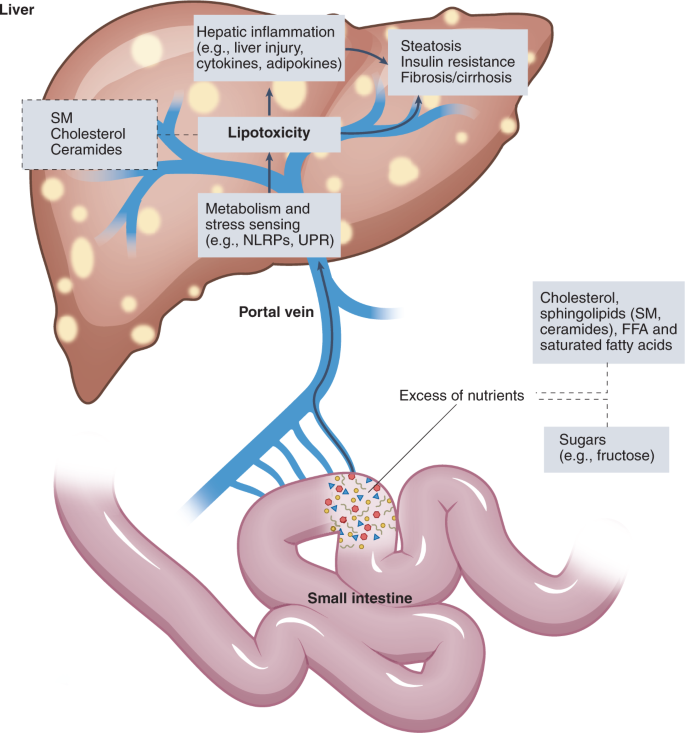
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity | Nature Metabolism

JCI - Parental metabolic syndrome epigenetically reprograms offspring hepatic lipid metabolism in mice
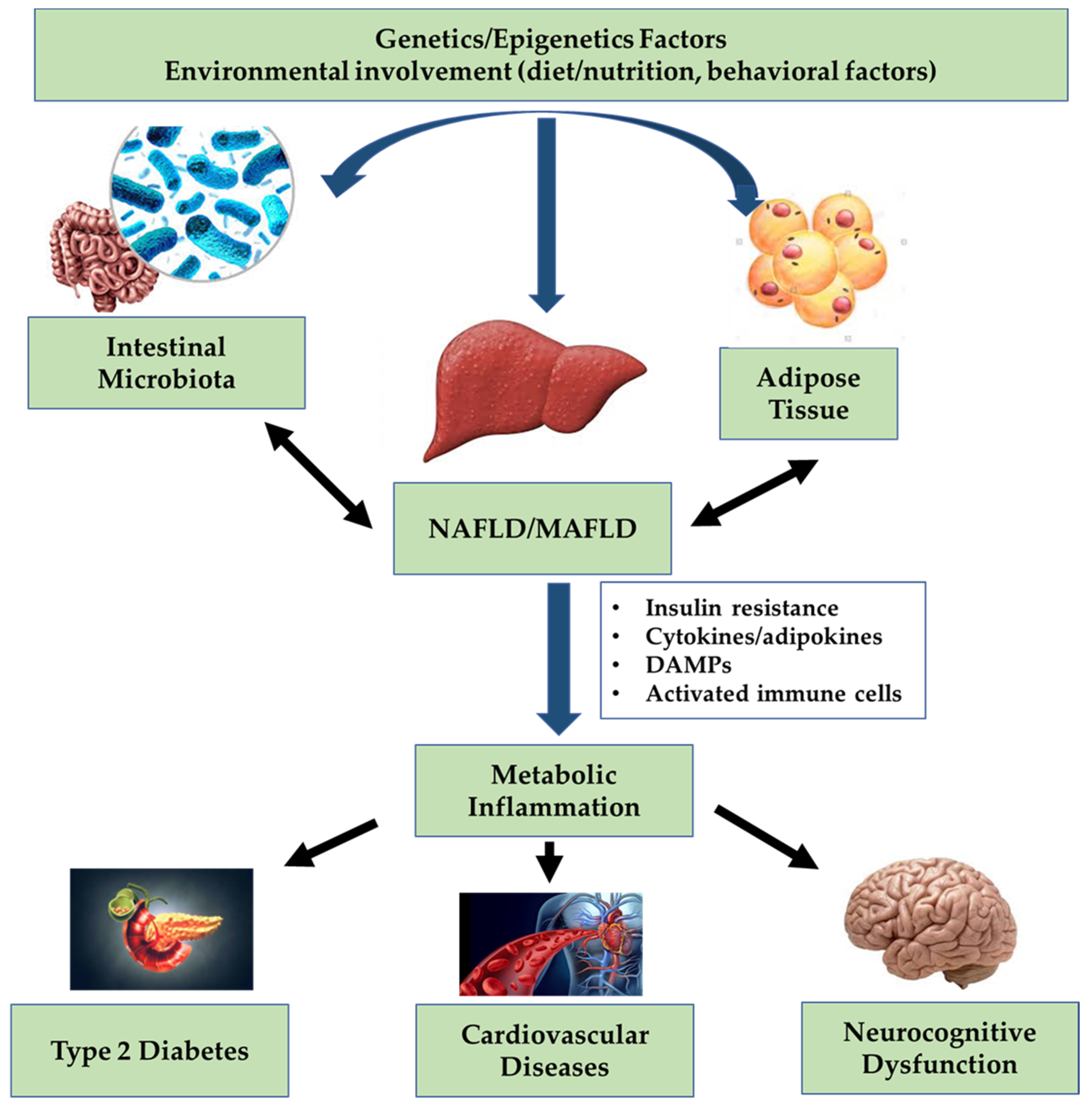
Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | Mechanisms of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Metabolic Syndrome. A Narrative Review

CRISPR-mediated BMP9 ablation promotes liver steatosis via the down-regulation of PPARα expression | Science Advances

Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease | Nature Reviews Nephrology