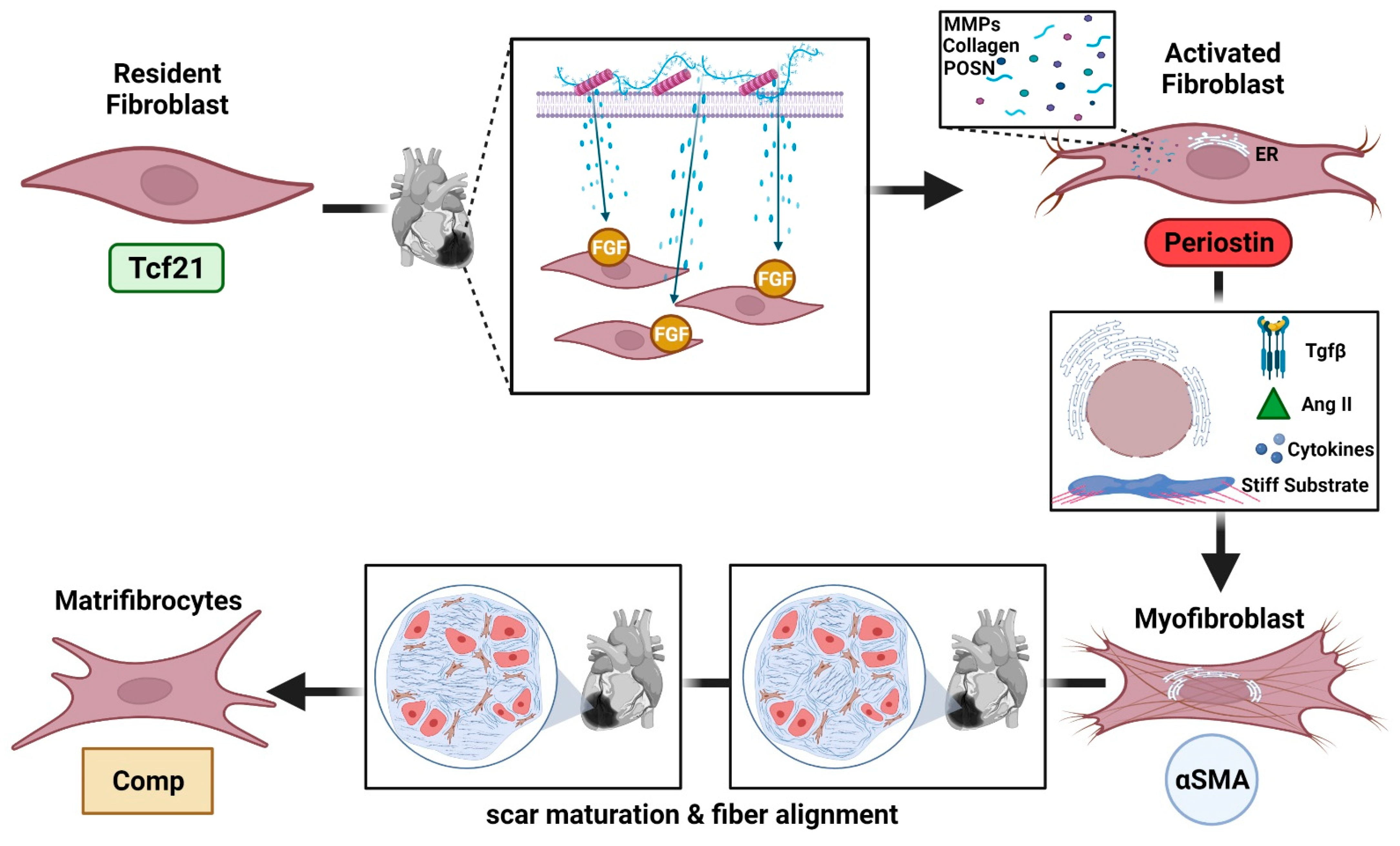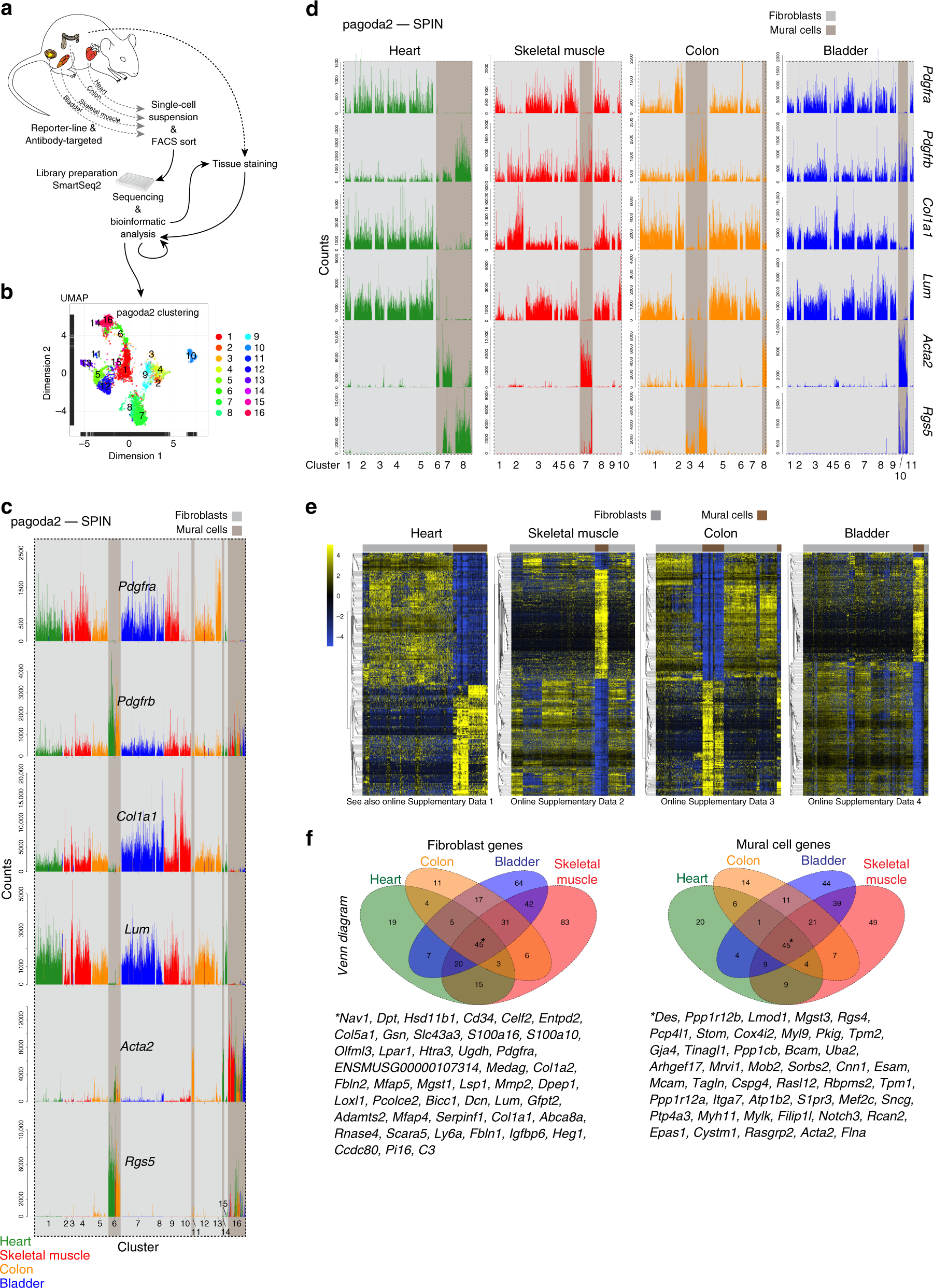
Single-cell analysis uncovers fibroblast heterogeneity and criteria for fibroblast and mural cell identification and discrimination | Nature Communications
CD44 Is a Negative Cell Surface Marker for Pluripotent Stem Cell Identification during Human Fibroblast Reprogramming | PLOS ONE

Characterization of dermal fibroblasts cell surface markers using flow... | Download Scientific Diagram

Definition and Signatures of Lung Fibroblast Populations in Development and Fibrosis in Mice and Men | bioRxiv
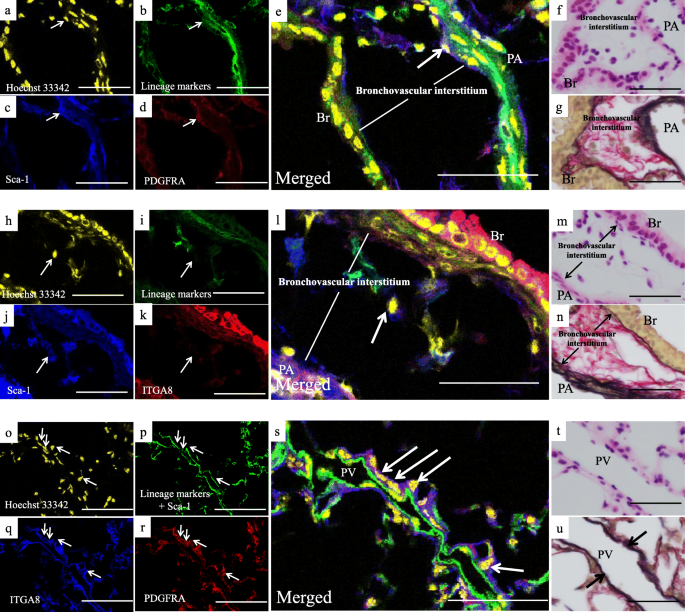
CD248 and integrin alpha-8 are candidate markers for differentiating lung fibroblast subtypes | BMC Pulmonary Medicine | Full Text
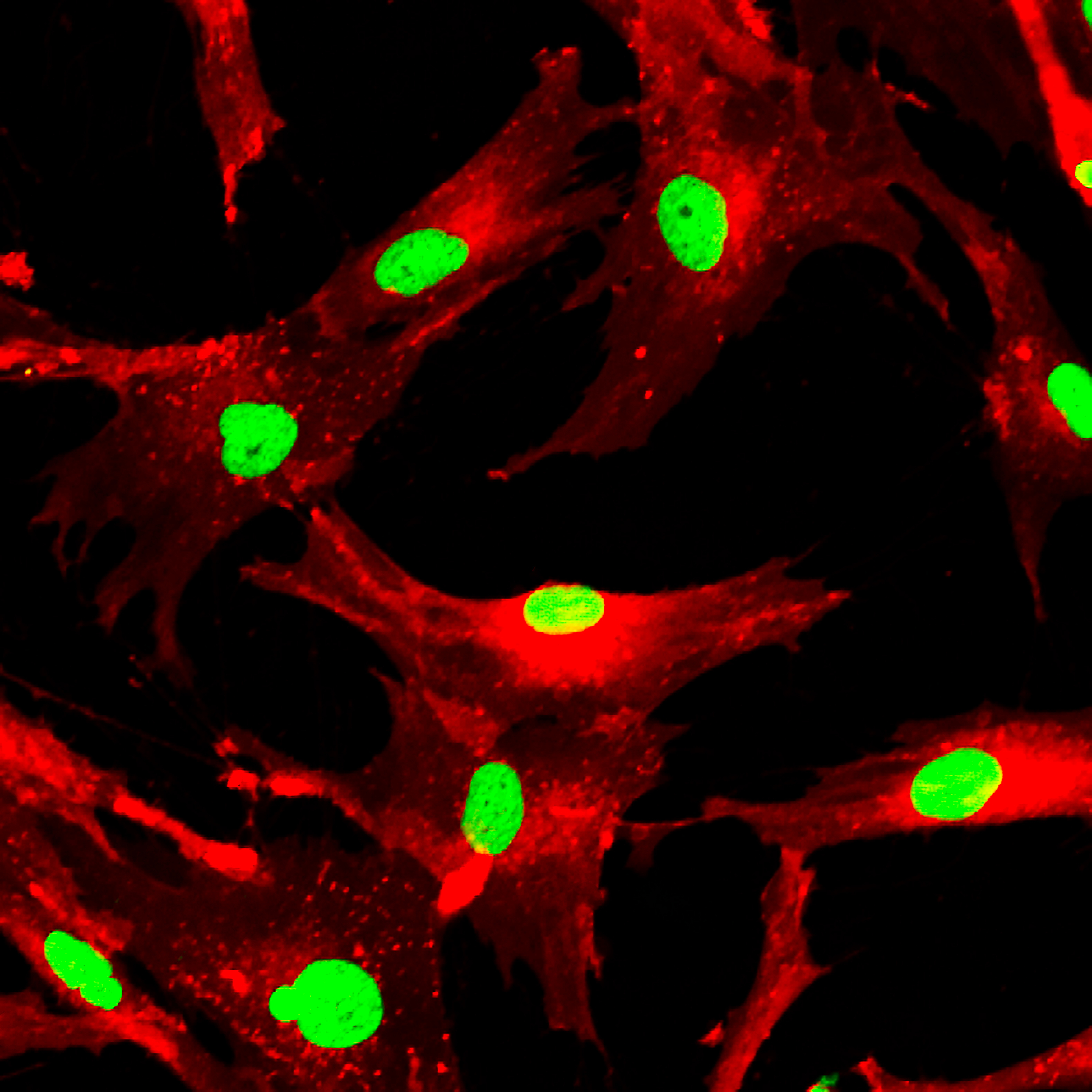
Cell Surface Marker on Lung Fibroblasts Seen to Indicate Disease Severity in IPF Patients | Pulmonary Fibrosis News

The fibroblast surface markers FAP, anti‐fibroblast, and FSP are expressed by cells of epithelial origin and may be altered during epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition - Kahounová - 2018 - Cytometry Part A - Wiley

Identification of a pro-angiogenic functional role for FSP1-positive fibroblast subtype in wound healing | Nature Communications
Flow cytometric characterization of cell surface markers to differentiate between fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells of diff

Generation of Quiescent Cardiac Fibroblasts From Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for In Vitro Modeling of Cardiac Fibrosis | Circulation Research
Flow cytometric characterization of cell surface markers to differentiate between fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells of different origin
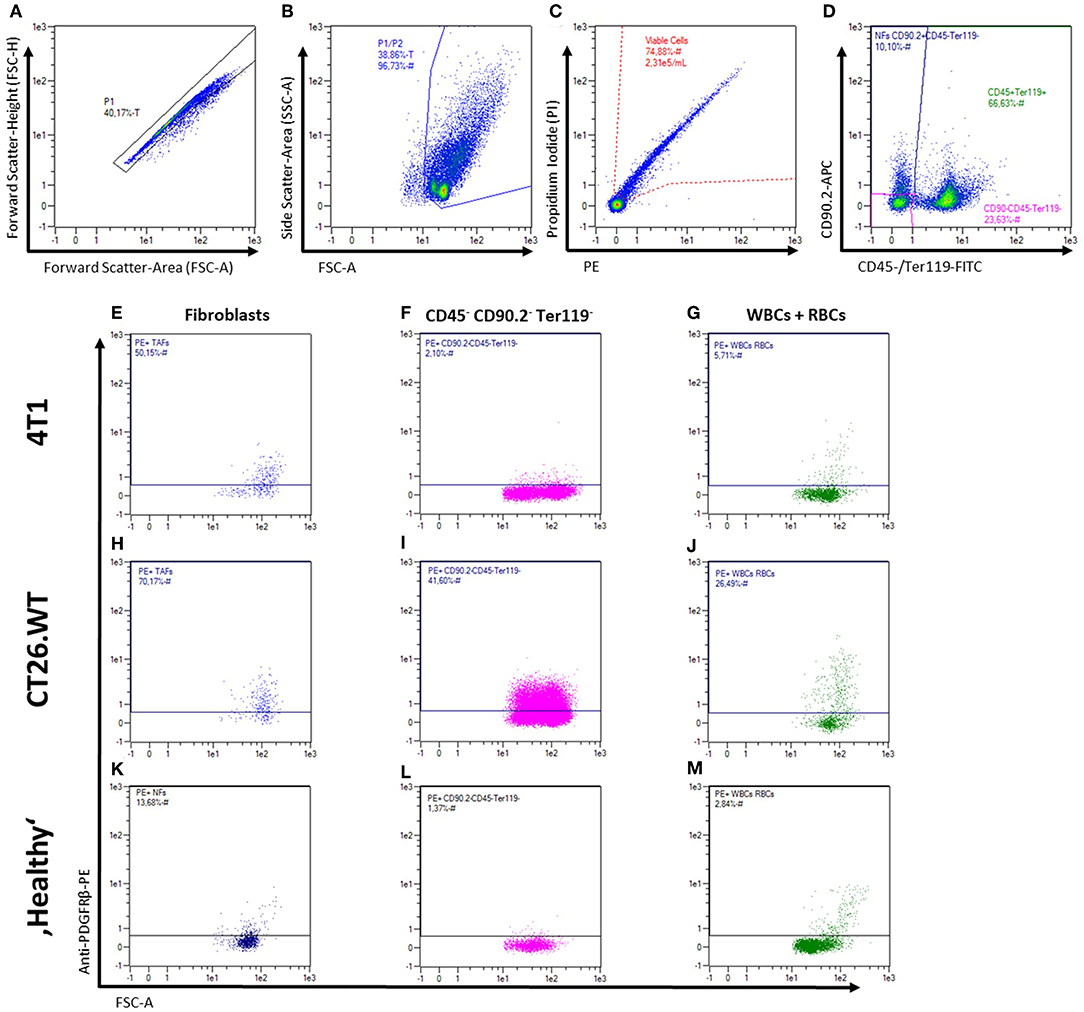
Frontiers | CD49b, CD87, and CD95 Are Markers for Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Whereas CD39 Marks Quiescent Normal Fibroblasts in Murine Tumor Models

The fibroblast surface markers FAP, anti‐fibroblast, and FSP are expressed by cells of epithelial origin and may be altered during epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition - Kahounová - 2018 - Cytometry Part A - Wiley

Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface marker expression in mouse... | Download Scientific Diagram

A) Flow cytometry analysis of fibroblast specific surface marker CD 90... | Download Scientific Diagram
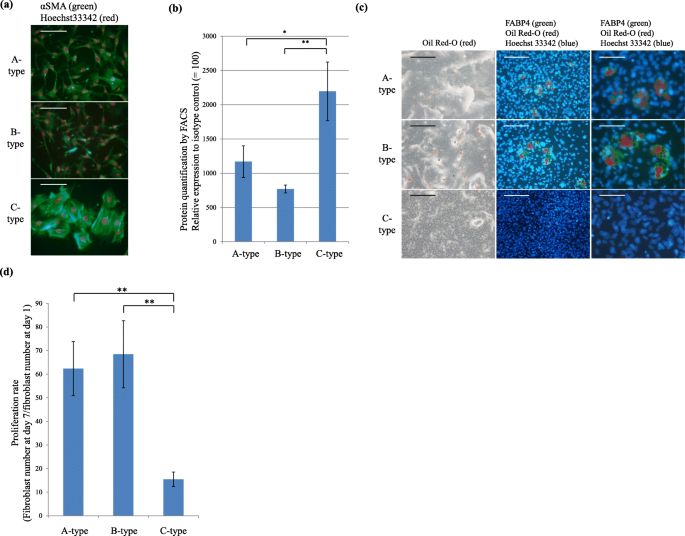
CD248 and integrin alpha-8 are candidate markers for differentiating lung fibroblast subtypes | BMC Pulmonary Medicine | Full Text
Cadherin-9 Is a Novel Cell Surface Marker for the Heterogeneous Pool of Renal Fibroblasts | PLOS ONE

Functionally distinct disease-associated fibroblast subsets in rheumatoid arthritis | Nature Communications