
CRISPR-Cas9 Editing Induces Loss of Heterozygosity in the Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis | mSphere

Oral mucosa as a potential source of candidemia by Candida parapsilosis sensu stricto, under pathological conditions

synteny of SAP genes of Candida albicans (Cal), Candida dubliniensis... | Download Scientific Diagram

The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source | mSphere
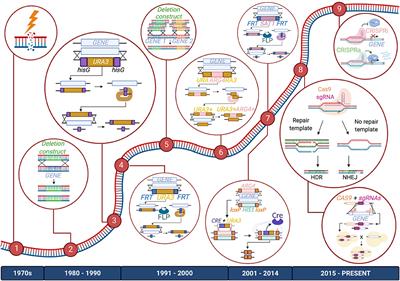
Frontiers | CRISPR-Based Genetic Manipulation of Candida Species: Historical Perspectives and Current Approaches
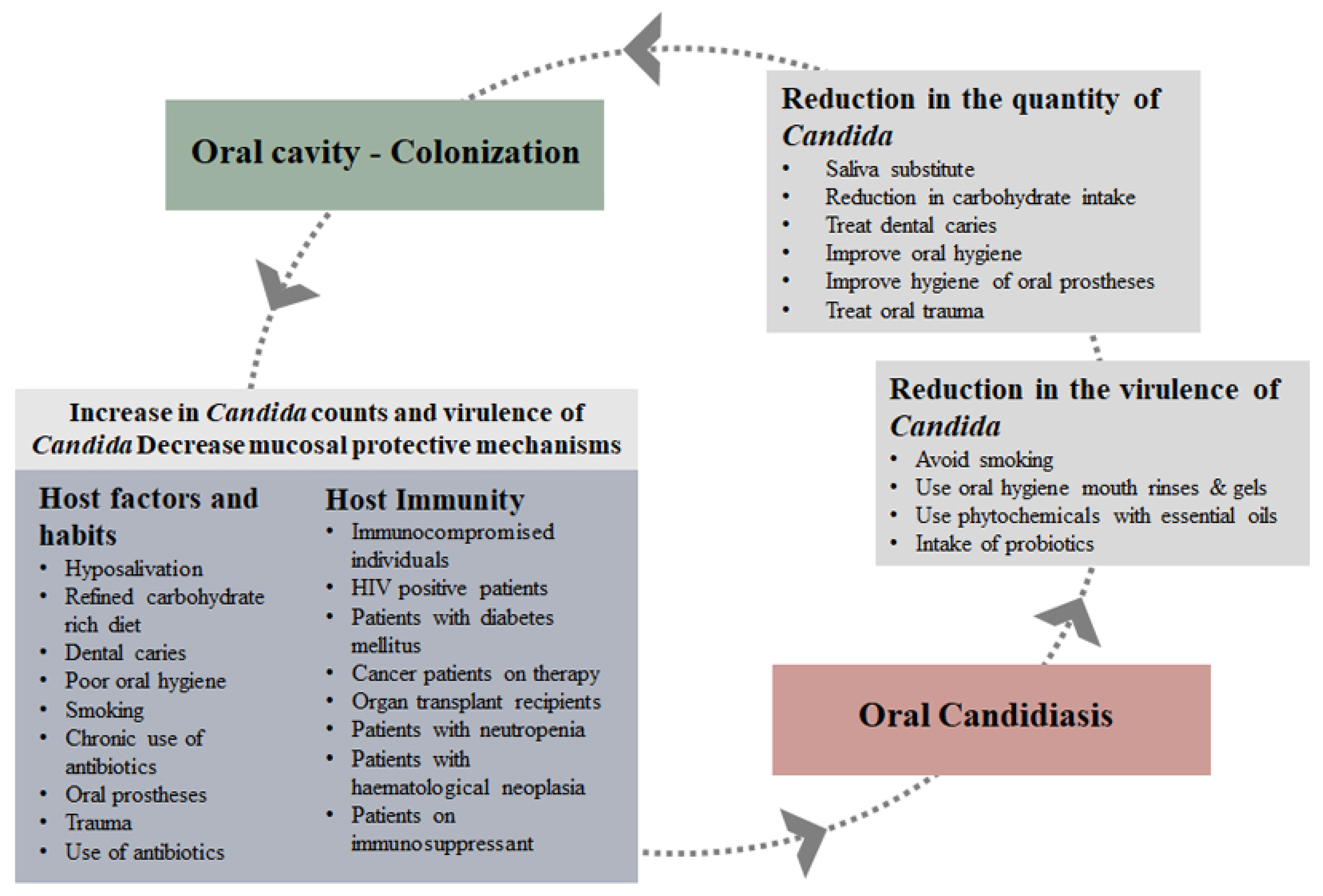
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Oral Cavity and Candida albicans: Colonisation to the Development of Infection

The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source | mSphere

The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source | mSphere
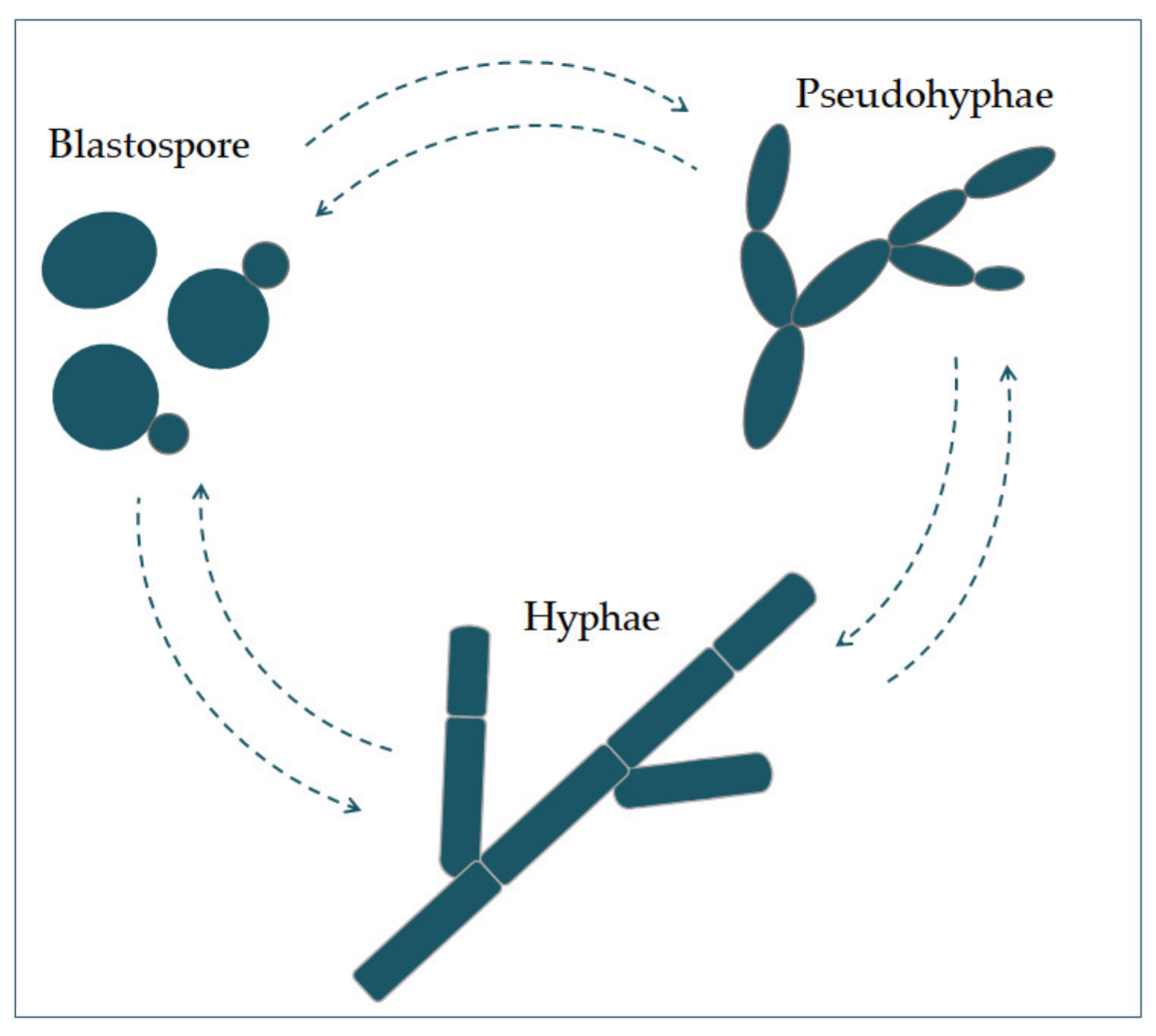
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection

CRISPR-Cas9 Editing Induces Loss of Heterozygosity in the Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis | mSphere
PDF) The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source

The gut, the bad and the harmless: Candida albicans as a commensal and opportunistic pathogen in the intestine - ScienceDirect

PDF) The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source
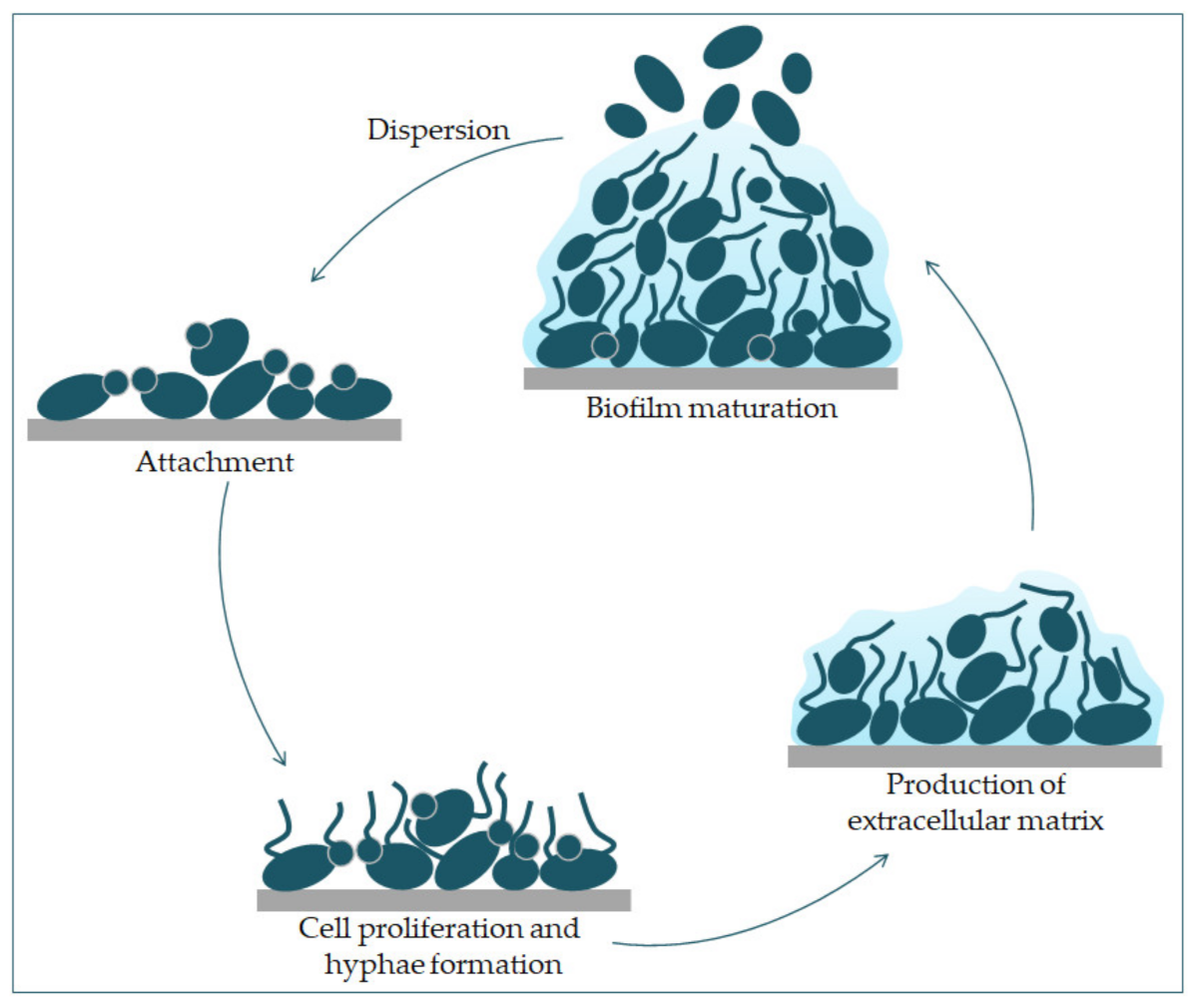
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection

The Pathogenic Yeast Candida parapsilosis Forms Pseudohyphae through Different Signaling Pathways Depending on the Available Carbon Source | mSphere

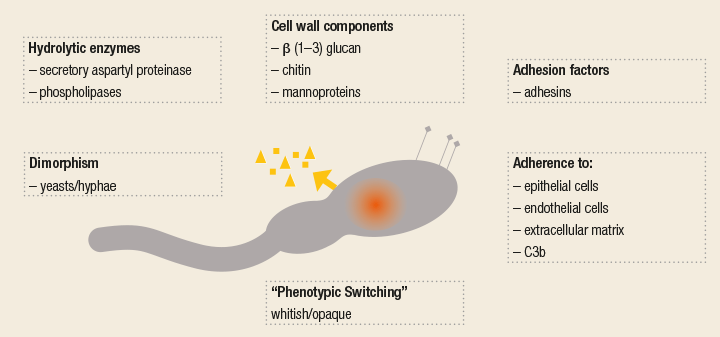


![PDF] Virulence factors of Candida species. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Virulence factors of Candida species. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8a957ac071588afa8187fce6e70308edd0a692ab/2-Figure1-1.png)


