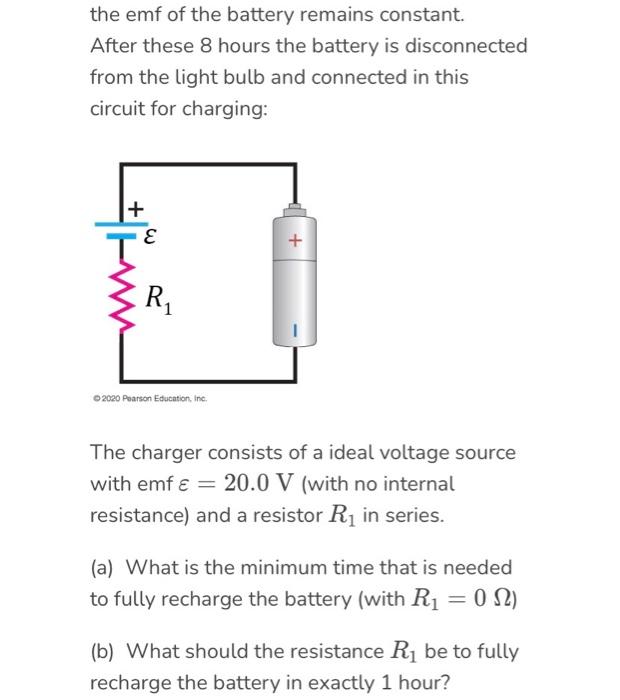
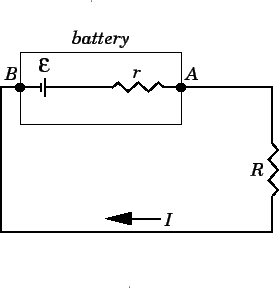
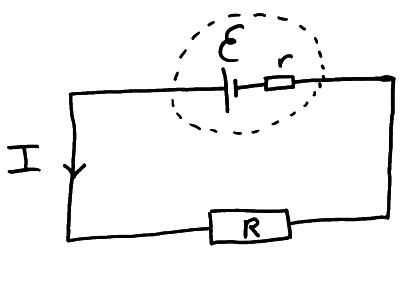
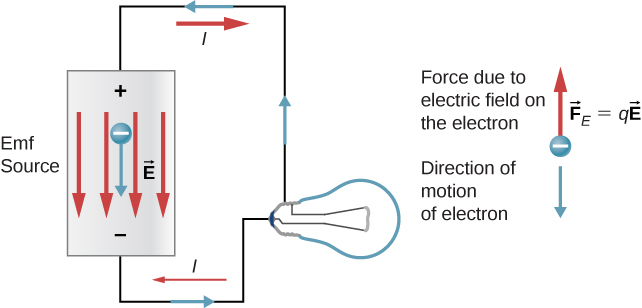
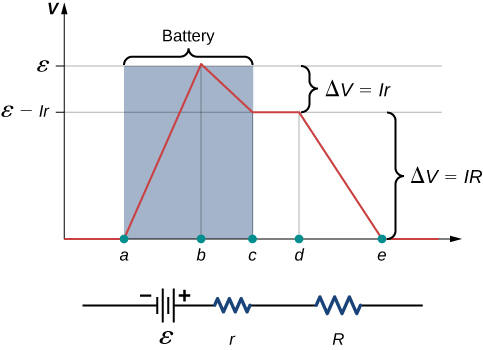
E.M.F. vs. Terminal Potential Difference (3.17) | Edexcel A Level Physics Revision Notes 2017 | Save My Exams
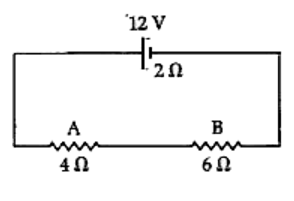
A battery of e.m.f. 12 V and internal resistance 2 Omega is connected with two resistors A and B of resistance 4 Omega and 6 Omega respectively joined in series. Find Electrical
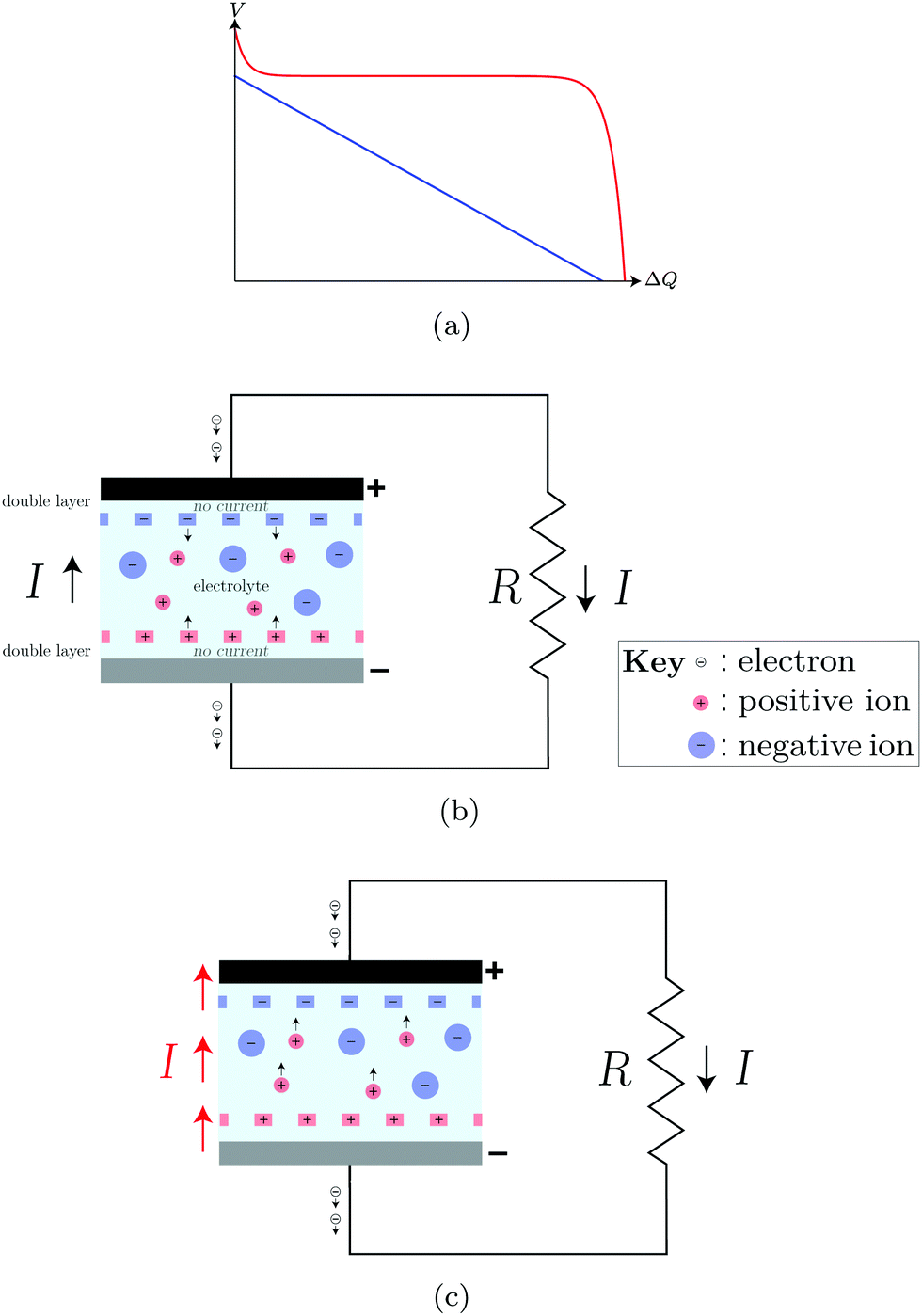
Dynamical theory for the battery's electromotive force - Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1CP00196E

A parallel plate condenser is charged by connecting it to a battery. Without disconnecting the battery, the space between the plates is completely filled with a medium of dielectric constant k. Then:
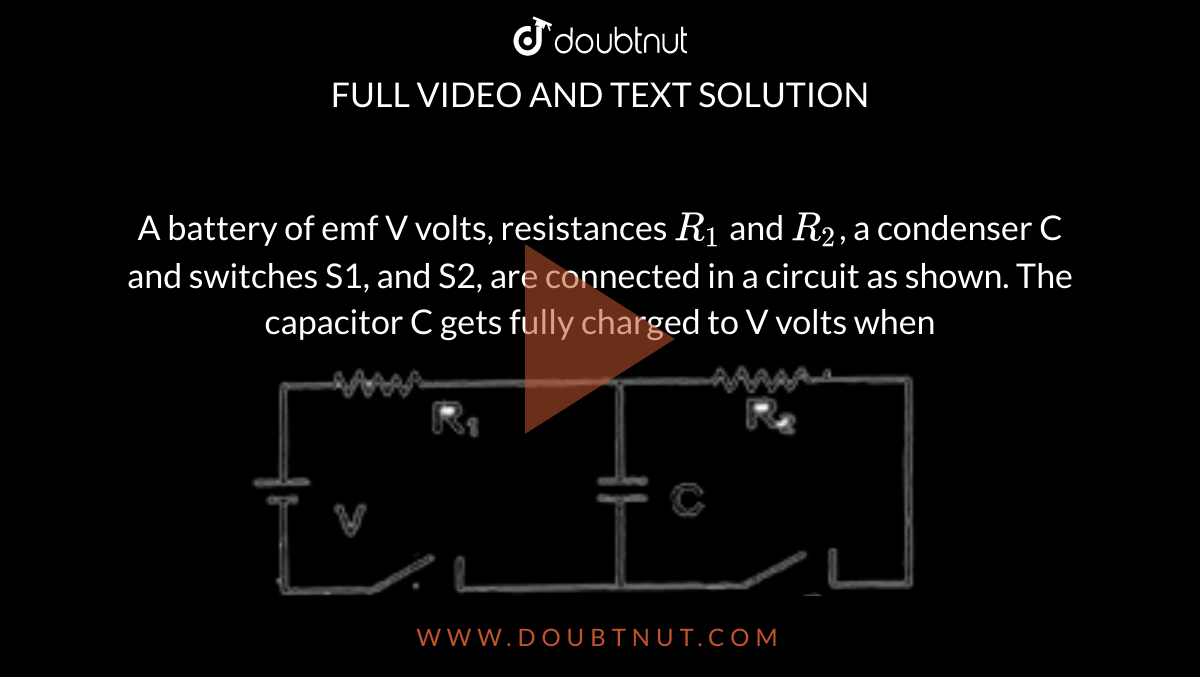
A battery of emf V volts, resistances R(1) and R(2), a condenser C and switches S1, and S2, are connected in a circuit as shown. The capacitor C gets fully charged to